An important diagnostic tool to measure the overall health of an individual is the CBC Test. This Complete Blood Count (CBC) test is considered the most common type of test, prescribed by doctors in case one feels persistent signs of fever, fatigue, or stress.
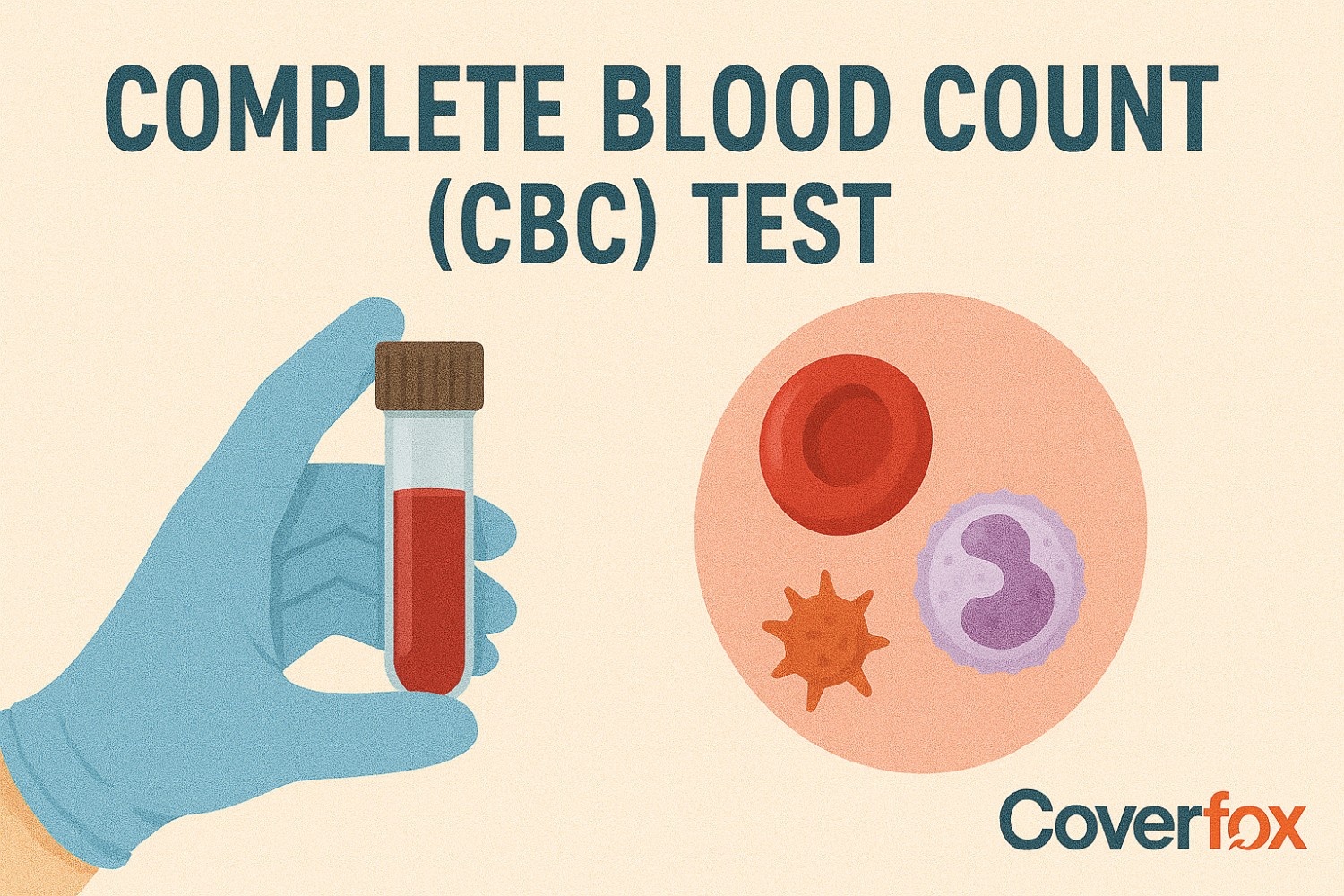
A normal CBC test, through a simple sample, analyses certain blood cells and determines results based on the criteria of a CBC blood test normal range. However, individuals need to understand how to assess these values in their blood report. To help in the knowledge of normal blood count and its ranges, the guide below provides detailed information about the same, allowing a better understanding of health and knowing when to seek medical advice.
What Is a Complete Blood Count (CBC) Test?
A CBC (Complete Blood Count) Test is a blood test taken routinely to analyse the three main types of cells in your blood: red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets. This analysis, done by a laboratory through your blood sample, helps diagnose potential health conditions like blood cancers, anaemia, infections, and other conditions—allowing a better assessment of overall health.
What are the Normal Ranges for CBC Parameters?
The total blood in the human body contains many vital blood cells measured by the CBC. Normal blood count ranges may vary depending on various factors. However, in general, for adults, the following table outlines the normal CBC test parameters:
| CBC Test Component | Normal Range for Adults |
|---|---|
| White Blood Cells (WBC) | 4,000 to 10,000 cells per mcL (4.0 to 10 k/mcL) |
| Red Blood Cells (RBC) | Females (or those taking estrogen): 4.0 to 5.4 million cells/mcL Males (or those taking testosterone): 4.5 to 6.1 million cells/mcL |
| Haemoglobin (Hb) | Females (or those taking estrogen): 11.5 to 15.5 g/dL Males (or those taking testosterone): 13 to 17 g/dL |
| Hematocrit (Hct) | Females (or those taking estrogen): 36% to 48% Males (or those taking testosterone): 40% to 55% |
| Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) | 80 to 100 fL (femtoliters) |
| Mean Corpuscular Haemoglobin (MCH) | 27 to 31 pg (picograms) per cell |
| Mean Corpuscular Haemoglobin Concentration (MCHC) | 32 to 36 g/dL |
| Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) | 12% to 15% |
| Platelet Count | 150,000 to 400,000 cells per mcL (150 to 400 k/mcL) |
| Mean Platelet Volume (MPV) | 7.0 to 9.0 fL |
| Neutrophils | 2,500 to 7,000 per mcL (2.5 to 7.0 k/mcL) |
| Lymphocytes | 1,000 to 4,800 per mcL (1.0 to 4.8 k/mcL) |
| Monocytes | 200 to 800 per mcL (0.2 to 0.8 k/mcL) |
| Eosinophils | Less than 500 per mcL (0.5 k/mcL) |
| Basophils | Less than 300 per mcL (0.3 k/mcL) |
| Immature Granulocytes | Less than 100 per mcL (0.1 k/mcL) |
| Nucleated Red Blood Cells (NRBC) | Less than 10 per mcL (0.01 k/mcL) |
Factors That May Affect CBC Values
Have a look at certain factors that can play a role in affecting the value of CBC:
The Type of Laboratory
Age of the Individual
Hormone Levels
Pregnancy and Health Conditions
Measurements Taken
Based on the laboratory that conducts the test, it may have a different standard of normal range that it considers.
Age plays a crucial role, as normal ranges vary significantly between adults and children.
Whether you’re male or female can change what’s normal for you. If you take hormone treatments, your reference range might differ.
Being pregnant or having certain health problems can affect your blood count values.
Laboratories can use different units to present their results, such as “cells per microlitre” or “cells per microlitre times 1,000”, which can make the same result appear very different in reports.
Abnormal CBC Results: What They May Indicate
In case your test results did not come back within the normal blood level in the human body range as prescribed above, it can point to various health issues such as:
Red Blood Cells (RBC)
White Blood Cells (WBC)
Platelets
Low levels of RBC can lead to anaemia, while a high red blood cell count indicates erythrocytosis.
In case WBC is low, it may indicate bone marrow disorders, while a high count indicates inflammation, infection, or leukaemia.
If the platelet count is high, it can cause a condition called thrombocytosis, and a low count causes thrombocytopenia.
When is a CBC Test Recommended?
A normal CBC test is recommended for any of the following situations:
Routine Health Check-Up
Presence of Symptoms
Monitoring Severe Conditions
Assessing Treatment Effects
During Pregnancy
Pre-Surgery
As part of a general health exam to monitor overall health by assessing normal blood count.
If you experience persistent fatigue, fever, weakness, or unexplained bleeding or bruising.
To keep track of chronic health issues like kidney disease, autoimmune disorders, or cardiovascular diseases.
To evaluate the impact of chemotherapy or other medications affecting blood cells.
A regular test is conducted to monitor the health of both mother and baby.
Before an operation, to ensure there are no underlying blood-related problems.
CBC Test in the Context of Health Insurance
A CBC Test is often covered in health insurance policies. It is vital to check this aspect with your insurance provider before purchasing the policy. Since coverage depends on the type of policy you own, clarifying these details in advance is beneficial.
Head over to Coverfox to compare the coverage of various health plans from a set of renowned insurers, so you get a better idea of the choice you’re making!
How is the Complete Blood Count (CBC) Test Done?
The CBC Test is done through two simple steps:
Collection of Blood Sample
Analysis by Laboratory
For adults, the health provider cleans the arm and then inserts the sterile needle into the vein. For infants, it may be done through a prick in the heel. The collected blood sample is stored in a vial for further testing.
The blood sample is sent to the laboratory for further analysis of normal blood levels in the human body, where a series of tests are conducted by a computer to determine the overall health of the patient.
After inserting the needle, the hand may be a little sore, which is why pressure is applied to this region and then secured with a gauze.
How to Interpret CBC Report: Tips for Patients?
Here are some tips for patients after receiving a CBC Report:
1. Compare Ranges
Once you receive the report, make sure to compare it with the normal CBC blood test ranges, as mentioned in the table above.
2. Avoid Panic
In case you see a mild deviation or one to two abnormal values in your report, do not panic and simply have a talk with your doctor.
3. Hydrate Yourself
Dehydration can have an effect on results, which is why effectively keep yourself hydrated before the test (unless the test demands otherwise).
4. Do not self-diagnose
Do not take matters into your own hands; if you see abnormal results, you should discuss them with your doctor.
To Conclude
A normal CBC test is a vital diagnostic tool to detect serious health conditions, providing an assessment of overall health. By knowing the normal blood count and understanding results, it helps in early detection and prevention of ailments, allowing you to make the right healthcare decisions!
Make sure your health insurance policy includes coverage for a CBC blood test well in advance. Go ahead and choose Coverfox as your trusted online medium to select the health insurance plan tailored to your needs, which is both cost-effective and secure!
Explore More:
Frequently Asked Questions
Does the CBC test require fasting?
Unless specifically mentioned by your healthcare provider, a CBC test generally does not require fasting.
What is the normal range for WBC count?
When assessing the normal blood level in the human body, the range for WBC count should be 4,500 to 11,000 cells/µL.
Can CBC detect serious diseases?
Yes. A normal CBC test can play an effective role in diagnosing conditions such as infections, cancers, anaemia, etc.
Is CBC covered under health insurance?
Yes, in general, many health insurance policies are known to cover CBC Tests. Based on specific policy, it is recommended to check this aspect in advance with the insurance provider.
What to do if CBC results are abnormal?
In case normal CBC test results are abnormal, do not panic or self-diagnose. Simply, contact your healthcare provider for further evaluation or the steps to be taken.