H3N2 is a highly contagious Influenza A virus causing prolonged fever, cough, body aches, and fatigue, with higher risks for children, the elderly, pregnant women, and people with chronic illnesses. Early diagnosis, rest, hydration, prescribed treatment, and timely medical care help manage symptoms and prevent complications. Preventive measures like annual flu vaccination, good hygiene, mask use, and avoiding close contact are key to staying safe.
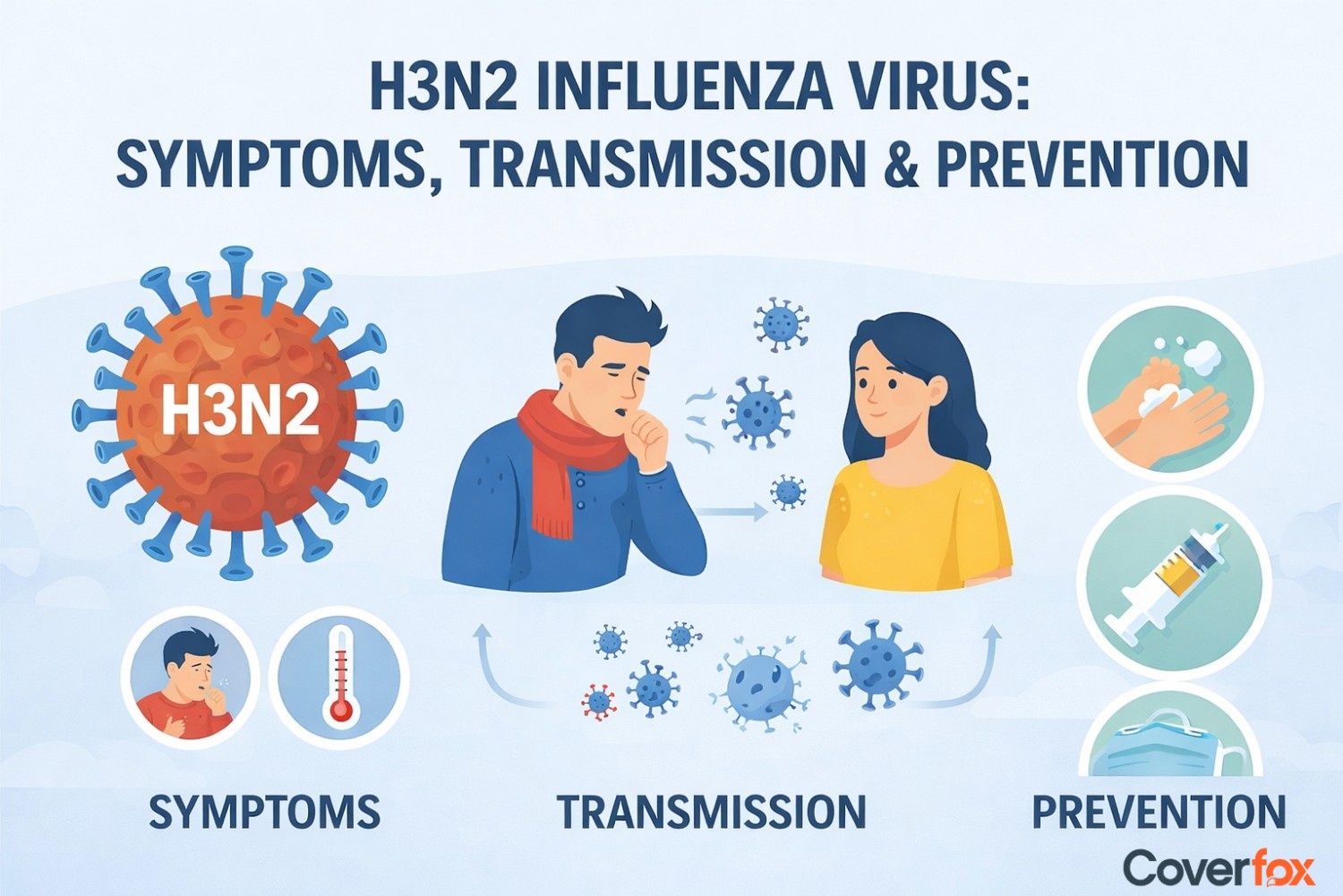
With a steep increase in cases of H3N2 flu, it is becoming essential to understand the signs and symptoms of this flu and how it spreads. This flu can lead to outbreaks and can prove to be serious, especially for young children, older adults, and those with weak immune systems. Mostly, people experience persistent fevers, severe coughs, body aches, and fatigue, and these symptoms end up lasting longer than usual, making recovery slower.
The guide below explores at H3N2 symptoms and treatment, as well as ways to protect yourself and stay safe.
What is the H3N2 virus?
Influenza A (H3N2) is a subtype of the seasonal influenza virus and is known to spread easily among humans. According to the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the virus primarily spreads through respiratory droplets released when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks, which can then enter the nose, mouth, or eyes of people nearby. The World Health Organisation (WHO) also states that influenza viruses can spread through contact with contaminated surfaces, followed by touching the face. In India, guidelines from the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) similarly highlight droplet transmission as the major mode of spread, with surface contamination being a secondary but possible route.
H3N2 influenza virus symptoms include:
Fever and feeling very cold and shivery
Swollen lymph nodes (in children)
Abdominal pain or discomfort
The nose feels blocked, and it is hard to breathe
Muscles and joints hurt
Coughing a lot (up to 2 weeks) and feeling throat pain
Pain or heaviness in the head (headaches)
Risk Factors for Complications
After observing what the H3N2 virus is, let us see that certain groups are at high risk of catching this flu and need to take more precautions. These include:
- Young children below 5 years old are more likely to develop serious flu problems.
- Older adults aged 65 and above have a higher chance of flu complications.
- Pregnant women need extra care, as they are at risk.
- People with long-term health issues like asthma, diabetes, heart disease, weak immune systems, or brain-related conditions have a higher risk of complications from H3N2 flu.
Also Read - Tips for a Healthy Heart & Controlling Cardiovascular Diseases
How Long Does H3N2 Flu Last?
The duration of H3N2 flu varies from person to person, depending on the severity of the infection and individual health conditions.
The H3N2 flu virus normally remains in the body between 5 and 7 days. Human beings are infectious until about five days after the onset of symptoms.
Most recoveries take a week, but cough and fatigue can take two weeks or more in severe cases.
It can take some individuals as short as five days to begin feeling better, although the recovery period can take different times depending on the severity of the illness.
How do Doctors Know Whether You Have the H3N2 Flu?
Below are the methods doctors use to identify and confirm an H3N2 flu infection.
- Doctors initially examine the symptoms to suspect H3N2 flu, as other viruses, such as COVID-19 and cold viruses, can share similar symptoms.
- Testing is done by a swab of your nose or throat.
- The RT-PCR test is a test that is used to detect the presence of the genetic material of the virus in the swab sample.
- The confirmation of the infection is done through culturing the virus in a lab.
- Blood tests are done to determine the antibodies that your body produces against the virus.
Also Read - Most Common Diseases in India Their Impact on Health Insurance
How Do You Treat H3N2 Flu?
Below are the recommended treatment measures and care practices used to manage H3N2 flu symptoms and prevent complications.
The following are the different treatment options that can be used against the H3N2 flu:
When you are ill, see a doctor to be adequately diagnosed and treated, and you might have to check your temperature and vital signs at home, as recommended by a doctor. Take enough water to loosen mucus and soothe throats.
Consume vitamin C/zinc-rich foods such as fruits to enhance immunity, and avoid dairy products, as they aggravate phlegm. Warm salt water (1/4 tsp, 8 oz, 2-3x/day) to relieve swelling, but do not overuse, as it can damage the enamel.
Steam inhalation can relieve coughs, but watch out for burning. See a doctor if persistent.
Take medications as prescribed by your physician. Do not prescribe any medications independently, particularly antibiotics or antiviral medications, as they may have side effects and are unnecessary.
Get immediate medical attention if there is an extremely high fever, shortness of breath, or saturation of oxygen (SpO2) under 94. These can be an indication of severe respiratory infections that need urgent treatment. Do it to protect yourself: keep yourself abreast with flu vaccinations, which make it less severe and less transmissible. Treatments: Antiviral therapy may be useful when used early.
Adhere to the recommendations of public health during outbreaks, such as wearing masks and social distancing. To learn more, refer to reputable sources, including the CDC or WHO websites.
How Can You Protect Yourself From the H3N2 Flu?
To protect yourself from H3N2 influenza virus symptoms, here are certain dos and don’ts you should follow:
| Do’s | Don'ts |
|---|---|
| Follow respiratory etiquette: cover nose and mouth with a tissue or handkerchief when coughing or sneezing, and wear a mask when outside. | Avoid touching your nose, mouth, or eyes, especially when outside. |
| Practice good hand hygiene, which means washing your hands well with soap and water regularly. | Avoid close contact with people who are sick. |
| Isolate yourself if you feel unwell. | Do not self-medicate or take medication without consulting a doctor. |
| Get vaccinated every year to protect yourself. | Avoid spitting in public places. |
| Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated. | Avoid shaking hands with people. |
| Avoid touching your mouth and nose with unclean hands. | Avoid eating in crowded places while sitting close to others. |
Summary
H3N2 is very contagious, but it can be treated and managed if identified early. Knowing the symptoms and treatment options is vital to prevent the spread and severity of the disease. Take effective measures, which include avoiding contact, practising personal hygiene, and getting vaccinated annually, to reduce the risk of getting infected.
As H3N2 may be aggravated in some groups, including young children, elderly individuals, and pregnant women, as well as individuals with underlying illnesses, a good health insurance policy becomes particularly vital. It assists in meeting hospitalisation bills, diagnostic checkups, emergency treatments, and doctor visits in case of complications caused by the flu. Good health coverage will make sure that you receive treatment promptly without the concern of paying the bills.
Also Read - Does Health Insurance Cover Swine Flu?
Frequently Asked Questions
Can someone catch the H3N2 flu again after recovering?
Yes, they can. The virus can mutate, which makes it difficult to avoid immunity built from past infections.
How many days does the H3N2 flu make you sick?
The H3N2 flu typically causes symptoms for about 5 to 7 days. However, residual effects like coughing and fatigue may persist for two weeks or longer, particularly in more severe cases.
Is H3N2 the same as swine flu?
No, H3N2 differs from swine flu, as it is a subtype of the Influenza A virus. H3N2 is believed to have originated in birds and was later transmitted to humans, while H1N1 (swine flu) originated in pigs and was then transmitted to humans.