Carcinoma is the most common type of cancer, originating in epithelial cells and affecting organs such as the skin, lungs, breast, liver, and kidneys. Early detection is crucial, as symptoms vary by type and stage, and timely diagnosis significantly improves treatment outcomes. Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and hormone therapy, often combined for better survival and quality of life.
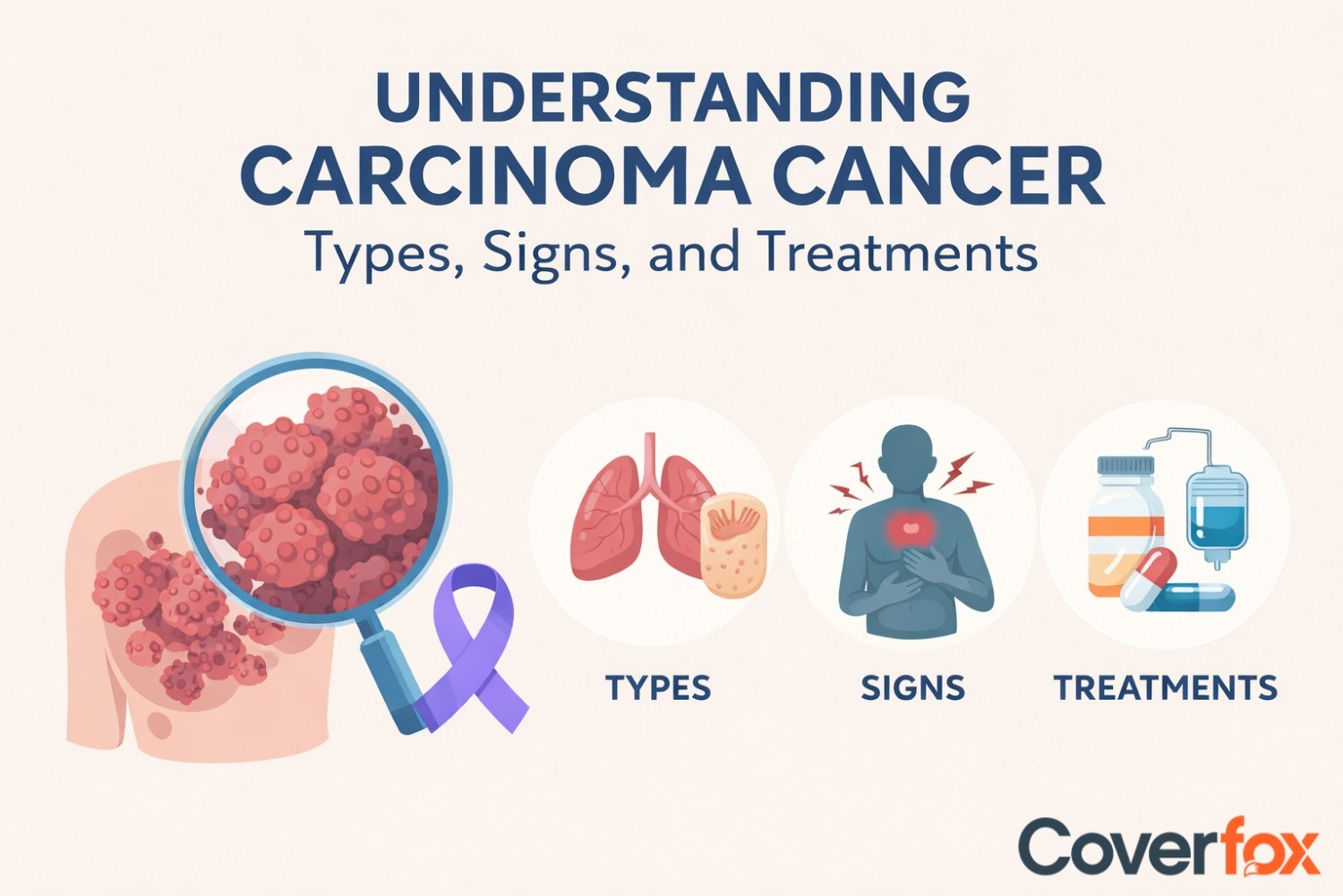
As per the National Cancer Institute, carcinomas account for 80 to 90% of all cancer cases worldwide. This is said to affect the tissues lining the various organs of the body, whether outer or inner, and it is said to be the most prevalent type. Carcinoma cells are said to gradually grow, multiply, and form tumours, which then go on to spread to different parts of your body. For this reason, early detection and treatment are important to improve chances of recovery.
The guide below takes a look at the various carcinoma types, along with their symptoms, as well as the various methods of treatment.
What is Carcinoma Cancer?
A common form of cancer, carcinoma cancer is said to originate in the epithelial cells that line the body's organs and tissues. Carcinoma cancer is said to affect various organs of the body, including the skin, breast, lungs, kidneys, and prostate. The abnormal cells of cancer multiply uncontrollably in the body, often spreading to other parts and developing tumours.
Different Types of Carcinoma Cancer
Based on the part of the body affected, carcinoma types can be divided into the following. These include:
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Adenocarcinoma
Renal Cell Carcinoma
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
This type develops due to frequent exposure of the skin to the sun. It forms in the innermost part of the skin's outer layer and does not spread to other parts. Basal cell carcinoma symptoms include red patches, scars, and bumps on the skin.
This type of tumour happens in the middle and outer layers of the skin, appearing as a scaly red patch, open sore, or wart-like growth. It can grow quickly, spread, and become life-threatening if not treated on time. The causes include sun exposure and weak immunity.
Developing in the hepatocyte cells of the liver, it is said to be a cancer of the liver. Early signs are not obvious, but later Hepatocellular Carcinoma symptoms may include losing weight or feeling pain in the belly. Certain risks behind it include hepatitis infections and heavy drinking.
This disorder is a cancer that begins in gland-forming epithelial cells found in organs such as the lung, colon, breast, and prostate. According to the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and CDC, major evidence-based risk factors include tobacco smoking (the strongest risk factor for lung adenocarcinoma), chronic inflammation (such as long-standing inflammatory bowel disease for colorectal cancer), obesity, and environmental/occupational carcinogens.
This is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults, making up about 90% of all cases. It starts in the kidney's tubules. Smoking and high blood pressure can increase the risk of this type, often showcasing symptoms like blood in urine, lower back pain, and sudden weight loss.
A common type of breast cancer that originates in the milk ducts of the breast and could spread to the surrounding tissue through the lymphatic system and bloodstream. Its exact cause is unknown, but certain contributing factors may be age, gender, hormonal issues, lifestyle habits, or even radiation exposure.
Signs and Symptoms of Carcinoma Cancer
The type of cancer and the specific area affected are important factors for determining the symptoms. Look out for the following:
- New or unusual growths or sores on the skin that fail to heal.
- Cough, which is not relieved, and difficulty in breathing (particularly in lung cancer).
- Weight loss without effort and a feeling of constant tiredness.
- Alterations in the frequency and quality of urination.
- Bloodless or bruised, unsuspected.
- Abdominal swelling, upper belly pain or discomfort, bloating.
- Swelling or lumps in the armpits or the breast.
- A bloody diarrhoea or urine.
You should visit a doctor to get a check-up in case you observe any of these symptoms.
Also Read - How Does a Cancer Insurance Plan Work?
Treatment Choices for Carcinoma Cancer
Depending on the stage, early detection always plays a key role in helping with treatment. These are the various types of cancer treatments that may be suggested by your healthcare professional:
| Treatment Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Surgery | Removal of the tumour or affected tissue through surgery is still a first-line treatment method, particularly in cases where the cancer is localised and has not spread. Cancers are better to be operated on at an early stage with higher chances of survival. Surgery can also be used in combination with the other therapies to enhance the prognosis. |
| Chemotherapy | This is a cancer treatment that involves anti-cancer drugs to kill or reduce the size of the cancer cells. It may be used as a neoadjuvant therapy (preoperative) to downsize the tumour or as an adjuvant therapy (postoperative) to decrease the recurrence risk. The side effects of chemotherapy are age and health dependent and occasionally necessitate the use of a different dose. |
| Radiation Therapy | Radiation uses high-energy beams, including X-rays, which are aimed at cancerous cells to kill them and prevent their proliferation. It is often combined with surgery and chemotherapy and helps to control the disease on a local level, and helps the victim to survive longer. Tolerance and side effects are dependent on the location of treatment, patient age and comorbidities. |
| Targeted Therapy | These are the drugs that are designed to attack certain genetic mutations or molecular weaknesses in cancer cells. They can be used with minimal side effects compared to chemotherapy since they can precisely target cancer mechanisms. Genetic testing is used to select candidates for targeted therapy, particularly in advanced or recurrent cancer. |
| Immunotherapy | Immunotherapy is effective by increasing the immune defences in the body, which identify and eliminate cancerous cells. It may not work for all patients, but it's a good alternative to some carcinomas. The side effects and benefits of immunotherapy vary according to the subtype of cancer and the immune status of the patient. |
| Hormone Therapy | Hormonal agents decrease or inhibit hormones that promote hormone-sensitive cancer, such as breast or prostate cancer. This treatment retards the progression of cancer and improves survival, but needs to be monitored and managed over a long period. |
Additional Considerations
The following highlights important factors influencing carcinoma outcomes, including prognosis, symptom variation, lifestyle habits, and the impact of existing health conditions.
Prognosis and Survival
Prevention and Lifestyle
Comorbidity Impact
The disease's prognosis and survival are generally higher in early-stage carcinoma, as it is localised and responsive to treatment. Later stages can be treated with multimodal therapies and are more pessimistic. Symptom Variation: The symptoms may change depending on age, gender, tumour location, and co-morbidity with other health conditions. As an illustration, cancer associated with hormones manifests differently in men and women; in the elderly, it may manifest in a less apparent way.
Lifestyle interventions, including avoiding tobacco, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, exercising, drinking alcohol in moderation, and using UV radiation protection, can help decrease the risk of certain carcinomas. Family history and awareness of family history are also important factors in early screening.
The presence of existing chronic diseases (such as diabetes and heart disease) may influence tolerance to treatment and its outcomes and require a different approach.
This holistic view enables patients and carers to have a better view of the treatment available, prognosis, and proactive measures that can help them recover and maintain long-term health.
Also Read - Cancer Insurance or Critical Illness Policy: Which Is More Beneficial
Bottom Line
Carcinoma can look different depending on where it starts, but catching it early and starting treatment—like surgery, radiation, or chemo—really boosts your chances of recovery. And honestly, dealing with cancer is tough enough without worrying about money. Having cancer health insurance alleviates financial stress by covering costs from the initial diagnosis to every subsequent checkup, thereby preventing the depletion of your savings.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most common type of cancer?
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) is said to be the most common type of cancer and is caused by excessive exposure to the sun on the skin.
Is it possible to cure the carcinoma cancer?
Yes, it can, with the help of many treatment options such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy, etc. Nonetheless, early identification of the disease is necessary to ensure a more effective treatment procedure.
Does health insurance cover cancer treatment?
Although the majority of health insurance plans include treatment of carcinoma, the coverage may differ. It is always prudent to seek confirmation with your insurance company before getting a policy.