Common Rail Direct Injection is a modern diesel technology that delivers high-pressure fuel through a common rail for precise, multi-stage combustion. It improves fuel efficiency, power delivery, noise levels, and reduces emissions compared to traditional diesel engines. CRDi systems are widely used across vehicles and continue to evolve with cleaner, high-pressure, and future emission-ready designs.
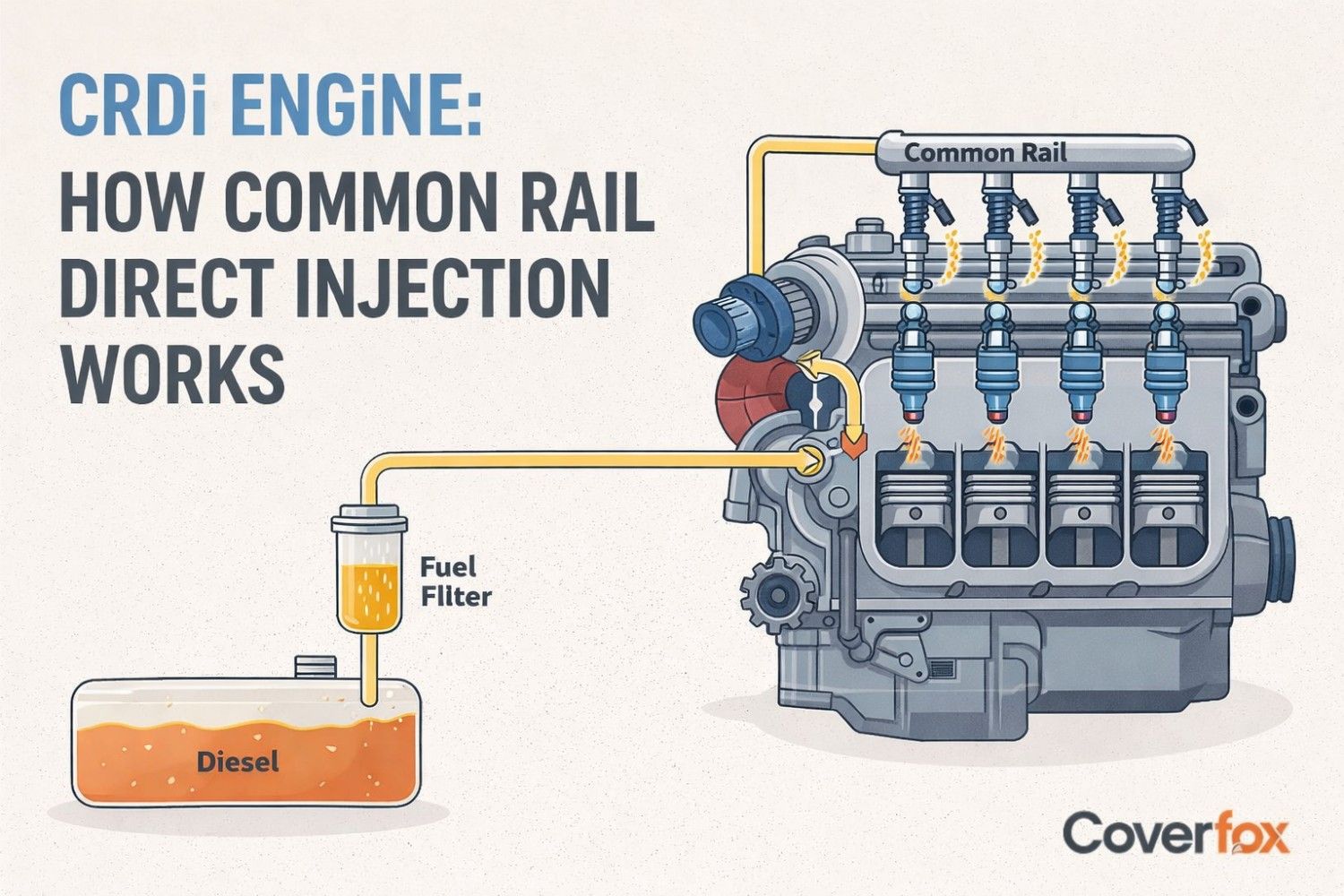
The CRDi engine has become common in present-day diesel vehicles, mainly because it gives steady power with lower smoke and better fuel use. Modern diesel cars are dominated by CRDi engines that provide a fine fuel injection at 1,000–2,500 bars through a common rail that allows several injections (pre-, main-, and post-injection) to achieve optimal combustion. This provides 15-20% higher fuel efficiency, 20-30% fewer emissions (NOx, particulates), and less noise than conventional systems. Timing is controlled by the ECU to provide constant power and reduce smoke.
What is a CRDi Engine?
CRDi full form is Common Rail Direct Injection, which delivers high-pressure (1,000-2,500 bar) fuel to a common rail that facilitates precise multi-stage injections to enhance superior combustion control. ECU optimisation provides constant power at low smoke levels.
It is a diesel injection process that ensures fuel is at high pressure in a single common rail. The older diesel engines had two lines with a significantly lower pressure. The CRDi design enables the engine to burn fuel in a more controlled manner because the various injectors are fed by a single rail rather than the feed pipe to each injector.
Most modern diesel cars, vans, and trucks now use a CRDi system because of its stable performance, cleaner exhaust, and longer engine life.
How do CRDi Engines Work?
The working flow of a common rail direct injection system is quite organised. Fuel moves through a few stages before reaching the cylinder:
CRDi Fuel Delivery pulls the diesel out of the tank through a high-pressure pump (up to 2,500 bar) and stores it in a common rail to supply it uniformly.
RPM (0-6,000), load (0-100%), intake air (MAF 0-500 g/s), and temperatures (ECT 20-120 o C, IAT -40-150 o C) are monitored in real-time by sensors.
ECU Function: 100+ sensor data per second to compute accurate injection timing (1-100 mm³/pulse), quantity (1-100 mm³/pulse), and pressure profile.
The injectors discharge 3-5 millisecond pulses, which atomise the fuel into 5-20 µm droplets, producing the ideal chamber.
This mix burns more evenly, which improves power and reduces extra smoke.
What are the Components of a CRDi Engine?
Common Rail Direct Injection systems depend on several important parts. Each part has its own task, and all must operate steadily:
Common rail: Holds highly pressurised fuel between 1,000 and 2,500 bars.
Injectors: Spray fuel inside the cylinder in controlled amounts.
Electronic Control Unit: Watches sensor data and decides the timing and duration of each injection.
High-pressure pump: Builds and maintains fuel pressure inside the rail.
If any of these parts fail, the engine may lose power or show difficulty starting.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CRDi Engines: Fuel Injection System Overview
Advantages
Better fuel use because fuel burns in a more even pattern
Lower soot and fewer harmful particles
Strong response at lower engine speed
Less sound and vibration than older diesel types
Smooth starting in cold areas
Disadvantages
Higher cost due to the use of precise parts
Needs skilled staff for most repairs
Sensitive to poor diesel quality
Injectors can wear faster
Repairs may need special tools
CRDi vs Traditional Diesel Engines
| Feature | CRDi Engine | Traditional Diesel Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel use | Higher efficiency | Lower efficiency |
| Noise | Smoother and quieter | Louder and more vibration |
| Cold start | More reliable | Often difficult |
| Emissions | Lower soot | Higher smoke |
| Power | Better response | Slower response |
This shows why vehicle manufacturers have moved towards a common rail layout.
What are CRDi Engine Applications?
CRDi systems are found in a variety of applications since they can provide high performance in a wide range of conditions:
Passenger cars: More mileage and less running.
Commercial vehicles: Trucks and buses consume less fuel when travelling over a long distance.
Farming machines: The system is used by tractors and harvesters during long hours of work.
Marine equipment: Fishing boats and small ships are dependent on a stable power supply.
Upcoming Future Trends in CRDi Technology
Research for CRDi advancements targets cleaner, lighter systems via ultra-high pressures (>2,500 bar, Bosch 2023) and dual-stage injections for 10-15% emission cuts. Hydrogen enrichment and nanoparticles boost efficiency 5-10% in prototypes. India eyes BS7 (Euro 7-based, mid-2025 rollout) mandating on-board monitoring and SCR integration:
Two-step injection patterns to reduce smoke further
Use of CRDi ideas in petrol engines
Designs that accept biofuel and hydrogen blends
Use of lighter metals to reduce engine weight
These trends may help reduce fuel burn and allow better control over emissions.
Summing Up
The CRDi system changed how modern diesel engines deliver fuel and burn it. The system offers improved fuel consumption, less smoke, smoother running, and stronger low-speed power. It is now a common choice for cars, vans, trucks, and many heavy-duty machines. CRDi engines may cost more to maintain, yet their long-term efficiency often appeals to drivers who want steady performance.
Many buyers also compare car insurance plans before choosing a diesel vehicle. Coverfox helps people study options from several insurers in one place. This tool helps users match coverage, features and costs before selecting a suitable plan.
Articles to Read:
Turbo Engines: How They Work, Benefits, Types & Tips
What is InLine Engine: Types and Applications
FAQs on CRDi Engines
Are CRDi engines more expensive to maintain?
CRDi Repairs demand trained technicians and specialised tools like diagnostic scanners (₹50,000+). Injectors (₹15,000-30,000 each) and sensors (₹5,000-12,000) exceed older diesel parts by 40-60% due to precision calibration. Annual service averages ₹8,000-15,000 vs. ₹4,000-8,000 for carbureted diesel parts.
Do CRDi systems require a specific type of diesel fuel?
They work best with clean diesel. Poor fuel can block injectors and lower pressure levels.
Are CRDi engines more environmentally friendly?
CRDi Emissions reduce particulate matter (PM) to 0.01-0.05 g/kWh (vs. 0.3-0.6 g/kWh in older mechanical diesels) through finer atomisation. NOx drops 20-40% to 0.2-0.4 g/kWh via precise multi-stage timing, though aftertreatment like SCR is often needed for full compliance. Soot visibility nearly vanishes compared to pre-2000 systems.
Can I retrofit a traditional diesel engine with CRDi technology?
Retrofit work is rarely worth the cost. It is better to choose a vehicle built with CRDi from the start.
Are CRDi engines suitable for all types of vehicles?
Yes. The system fits cars, heavy trucks, off-road machines and marine equipment.
What is the disadvantage of CRDi?
The disadvantages of Common Rail Direct Injection systems include high repair costs, fuel sensitivity, and injector wear.
Which engine is better, TDI or CRDi?
Both use direct injection. CRDi permits better control over timing and fuel amount, which improves power and emissions.
What is better, common rail or direct injection?
CRDi is an advanced form of direct injection, so it achieves higher pressure and more precise control.
Disclaimer: This article is meant for general informational purposes about CRDi engines and vehicle technology. It should not be considered mechanical advice or a substitute for professional automotive guidance. Engine performance, fuel efficiency, and maintenance costs may vary across manufacturers. Always consult a certified technician or the vehicle manufacturer for accurate technical recommendations.