The four-stroke engine is the backbone of modern cars, efficiently converting fuel into power through four distinct piston strokes. Known for fuel economy, low emissions, and smooth operation, it is the dominant engine design in the automotive industry.
In the heart of almost every modern car lies a marvel of mechanical rhythm, the four-stroke engine. Often described as the breathing soul of automobiles, this engine transforms fuel into motion through a perfectly timed cycle of intake, compression, power, and exhaust. Its intelligent design maximises fuel efficiency and performance while ensuring smoother operation and long-lasting reliability. The four-stroke engine has become the preferred choice for modern vehicles because it delivers the ideal balance of power, durability, and environmental efficiency.
At its core, a set of vital components such as pistons, valves, crankshafts, and spark plugs work together seamlessly to create the dependable performance that defines today’s cars.
What is a Four-stroke Engine in Cars?
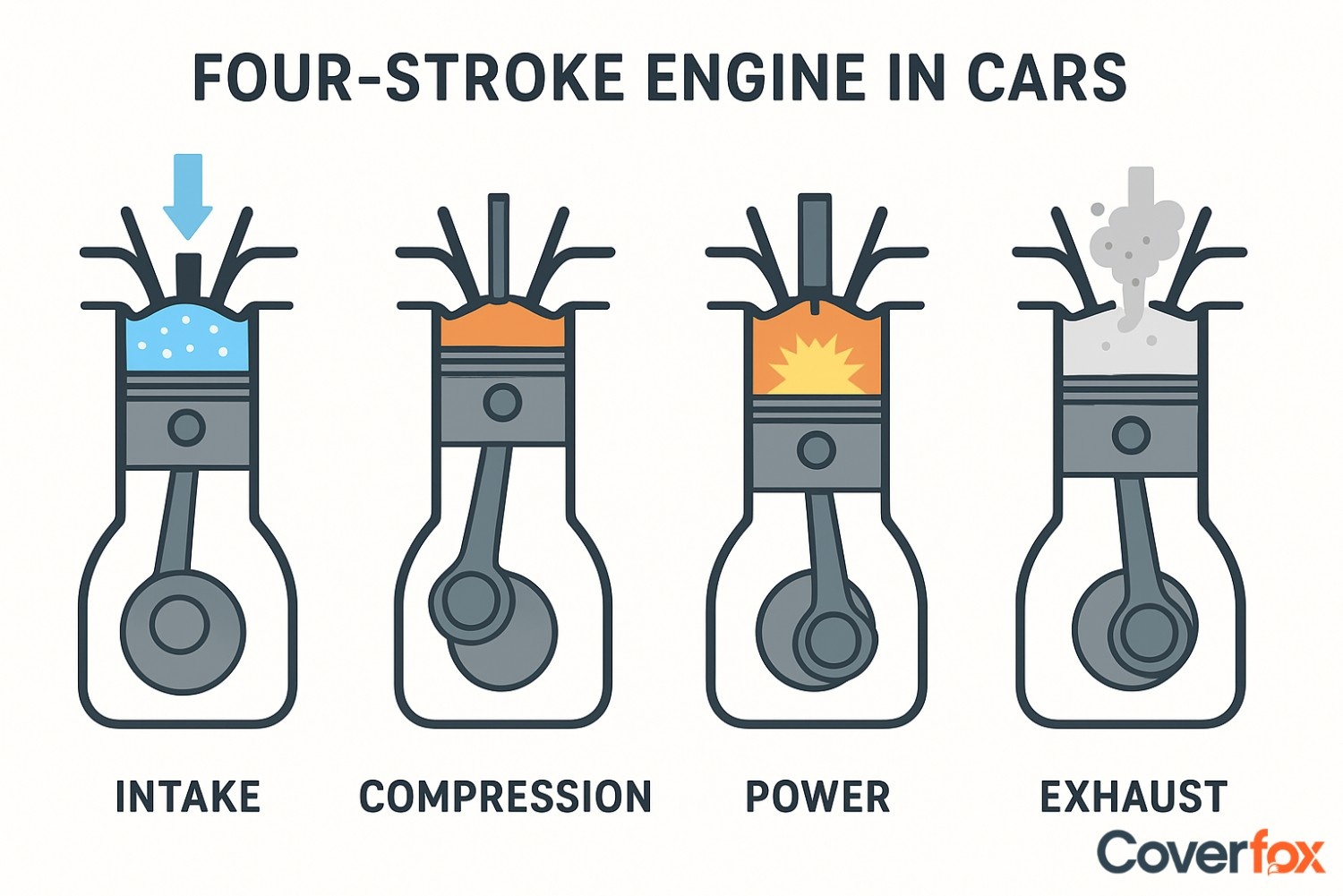
A four-stroke engine is an internal combustion engine widely used in cars and motorcycles for its efficiency and reliability. It operates through four piston strokes: intake, compression, power, and exhaust, which work together to convert fuel into mechanical energy. In the intake stroke, the piston moves downward, drawing in a mixture of air and fuel. During compression, the piston moves upward to compress this mixture, making it more combustible. The power stroke occurs when a spark ignites the compressed mixture, forcing the piston down and producing mechanical energy that drives the vehicle.
Finally, in the exhaust stroke, the piston moves upward again to expel burnt gases through the exhaust valve. This four-step cycle repeats continuously, ensuring smooth operation, improved fuel efficiency, and dependable performance in automobiles and motorcycles.
Key Parts of a Four-Stroke Engine
A four-stroke engine relies on a set of essential components that work together to convert fuel into mechanical energy efficiently. Each part has a specific role that ensures smooth operation, power generation, and fuel economy.
Cylinder and Piston
Crankshaft and Connecting Rod
Valves (Intake and Exhaust)
Spark Plug
Camshaft
Piston Rings
The cylinder is the core chamber where combustion occurs, and the piston moves up and down within it. The piston compresses the air-fuel mixture and transfers the force from combustion into mechanical motion, powering the engine.
The connecting rod links the piston to the crankshaft. When the piston moves, the crankshaft converts its linear motion into rotational motion, which ultimately drives the wheels of the vehicle.
(Fact: Typical crankshaft speeds in modern cars range between 600 and 6,000 RPM.)
Valves control the flow of gases in and out of the cylinder. The intake valve allows the air-fuel mixture to enter, while the exhaust valve releases burnt gases after combustion, ensuring smooth airflow and efficient engine cycles.
The spark plug ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture in petrol engines, starting the combustion process. This ignition generates the power stroke that pushes the piston downward, creating useful energy.
The camshaft regulates the timing of the valves, ensuring they open and close precisely in sync with the piston’s movement. Accurate valve timing improves fuel combustion and overall engine performance.
Piston rings provide a tight seal between the piston and cylinder walls, preventing gas leakage, maintaining compression, and reducing friction for smoother engine operation and longer lifespan.
Together, these components form a synchronised system that delivers reliable power, efficient fuel usage, and long-term durability. They are the key reasons why four-stroke engines dominate modern automotive design.
Advantages of Four-Stroke Engines in Cars
Four-stroke engines are the preferred choice for modern cars due to their superior performance, efficiency, and environmental benefits. Compared to two-stroke engines, they offer smoother operation and longer service life, making them ideal for everyday use.
1. Better Fuel Efficiency
Four-stroke engines burn fuel more completely during each cycle, ensuring optimal use of fuel and reducing wastage. This results in higher mileage and lower running costs compared to two-stroke engines.
2. Lower Emissions
Because combustion is more controlled and complete, four-stroke engines release fewer unburnt hydrocarbons and pollutants. They meet stricter emission standards, making them more eco-friendly than two-stroke engines.
3. Longer Lifespan
Four-stroke engines experience less wear and tear since they complete a power cycle in four strokes instead of two. This slower and smoother operation extends the engine’s durability and reduces maintenance needs.
4. Smoother and Quieter Operation
The balanced design of four-stroke engines allows them to run with less vibration and noise. This results in a more comfortable driving experience and stable engine performance over time.
5. Better Lubrication
These engines use a separate lubrication system, preventing oil from mixing with fuel. This not only enhances efficiency but also reduces smoke and engine damage caused by improper lubrication, which is common in two-stroke engines.
6. Environmentally Friendly Performance
With cleaner combustion, lower fuel consumption, and reduced exhaust emissions, four-stroke engines are far more sustainable and compliant with modern environmental regulations than two-stroke engines.
Overall, four-stroke engines outperform two-stroke engines in fuel economy, longevity, and environmental impact, making them the dominant choice in today’s automotive industry.
How Does a Four-Stroke Engine Work? (Step-by-Step Cycle)
A four-stroke engine converts chemical energy from fuel into mechanical motion through four coordinated strokes. Each stroke serves a unique purpose in maintaining power output, efficiency, and emissions control. This is a step-by-step Breakdown of the Four Strokes:
Intake Stroke
Compression Stroke
Power Stroke
Exhaust Stroke
During the intake stroke, the piston moves downward, creating a vacuum inside the cylinder. This allows the intake valve to open, letting the air-fuel mixture enter the combustion chamber from the carburettor or fuel injector. This step ensures the cylinder is filled with the precise mixture needed for combustion.
Once the intake valve closes, the piston moves upward, compressing the air-fuel mixture into a smaller space. This increases pressure and temperature inside the cylinder, preparing the mixture for efficient combustion. The higher the compression, the more power the engine can produce from the same amount of fuel.
In this stroke, the compressed air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark plug (in petrol engines) or by heat generated through compression (in diesel engines). The explosion forces the piston downward with great force, producing mechanical energy that turns the crankshaft. This is the only stroke that actually generates power in the engine cycle.
Finally, the piston moves upward again, pushing the burned gases out of the cylinder through the open exhaust valve. This clears the chamber of waste gases and makes room for a fresh charge of air-fuel mixture in the next cycle. Each of these four strokes works in a continuous sequence, ensuring that the engine runs efficiently and delivers steady power output.
Four-Stroke Engine vs. Two-Stroke Engine: Key Differences
Engines can be broadly categorised based on how they complete their power cycle. The four-stroke and two-stroke engines are the most common types, each with distinct designs and performance characteristics. Understanding their key differences helps in choosing the right engine for specific applications like cars, bikes, or machinery.
| Parameter | Four-Stroke Engine | Two-Stroke Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Power Stroke | Generates one power stroke for every four piston movements | Generates one power stroke for every two piston movements |
| Weight and Size | Heavier and larger because of more components | Lighter and smaller due to fewer parts |
| Fuel Efficiency | Highly fuel-efficient with complete combustion | Less fuel-efficient, as some fuel escapes during exhaust |
| Torque and Power | Delivers steady torque and smooth performance | Produces quick bursts of power but less consistent torque |
| Noise and Vibration | Operates quietly with minimal vibration | Louder operation with more vibration |
| Maintenance and Lifespan | Requires less frequent maintenance and lasts longer | Needs frequent maintenance and wears out faster |
| Repair Cost | Higher repair costs due to complex design | Lower repair costs but shorter lifespan |
| Applications | Commonly used in cars, motorcycles, and heavy vehicles | Used in scooters, chainsaws, and small machines |
In summary, four-stroke engines excel in efficiency, lifespan, and smooth performance, making them the preferred choice for modern automobiles. Two-stroke engines, while simpler and lighter, are better suited for compact, high-speed applications where quick bursts of power are needed.
Common Problems in Four-Stroke Engines (and How to Fix Them)
While four-stroke engines are known for their efficiency and durability, they can still face performance issues over time due to wear, improper maintenance, or fuel quality. Recognising common problems early can help prevent major engine damage and ensure smooth operation.
Engine Misfires
Overheating
Poor Fuel Economy
Engine Knocking
Loss of Power or Acceleration
A misfire occurs when one or more cylinders fail to ignite the air-fuel mixture properly. This can happen due to faulty spark plugs, clogged fuel injectors, or ignition timing issues. Misfires often cause rough idling, reduced power, and poor acceleration. If the issue persists despite basic checks, a professional diagnosis is recommended to prevent further engine strain.
Overheating is usually caused by coolant leaks, a malfunctioning radiator fan, or a blocked cooling system. Continuous overheating can warp the cylinder head or damage internal components. If your temperature gauge rises frequently or steam appears from the hood, stop driving immediately and have the cooling system inspected by a mechanic.
When a four-stroke engine starts consuming more fuel than usual, it could indicate dirty air filters, low tyre pressure, fuel injector issues, or incorrect spark timing. Regular servicing and timely replacement of filters can help, but if the fuel efficiency continues to drop, a professional tune-up may be necessary.
Knocking or pinging sounds from the engine usually occur when the fuel-air mixture detonates prematurely inside the combustion chamber. Common causes include low-quality fuel, carbon buildup, or incorrect ignition timing. Continuous knocking can lead to severe engine damage, so it’s best to have it checked and corrected promptly.
A noticeable drop in engine power can be linked to problems with the fuel system, clogged exhaust, or worn piston rings. Regular maintenance helps prevent this, but if power loss persists, professional inspection is advised to avoid internal damage.
When to Seek Professional Help:
Minor issues like dirty filters or low coolant can be fixed through basic maintenance, but if you notice repeated misfires, overheating, knocking, or significant power loss, it’s best to visit a certified mechanic. Early detection and repair can save major costs and extend the engine’s lifespan.
Expert Insight: Most four-stroke issues stem from poor maintenance, low-quality fuel, or overheating. Regular oil changes and coolant checks can prevent 80% of failures (AAA Research, 2023).
Final Thoughts
Understanding how a four-stroke engine works helps car owners maintain performance, improve fuel economy, and recognize early signs of engine wear. Regular maintenance — such as timely oil changes, air filter replacements, and coolant checks — can extend engine life by up to 40% (AAA, 2023).
Keeping your engine healthy not only enhances driving comfort but also reduces emissions and repair costs. Having a comprehensive car insurance policy can provide additional peace of mind in case of unexpected engine repairs. If you’re unsure about complex issues like knocking or overheating, consult a certified mechanic for diagnostics.
Related Articles:
Thermostatic Valves in Car Engines: Function, Types and Maintenance
Difference Between 3-Cylinder Engine and 4-Cylinder Engine
What is InLine Engine: Types and Applications
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is a four-stroke engine?
A four-stroke engine is an internal combustion engine that completes one power cycle through four stages called intake, compression, power, and exhaust to convert fuel into mechanical energy.
Why is a four-stroke engine popular in cars?
It is widely used in cars because it offers high fuel efficiency, lower emissions, smooth operation, and long-lasting performance compared to other engine types.
What are the main components of a four-stroke engine?
The key parts include the cylinder, piston, crankshaft, connecting rod, camshaft, valves, spark plug, and piston rings — all working together to generate smooth power output.
How does a four-stroke engine work in a car?
It works through four stages — intake, compression, power, and exhaust — that convert fuel into motion. The power stroke drives the crankshaft, creating mechanical energy that moves the car.
Can a four-stroke engine run on both gasoline and diesel?
Yes, but the design differs. Petrol engines use spark ignition, while diesel engines rely on compression ignition, though both follow the same four-stroke cycle.
What causes a four-stroke engine to overheat?
Overheating can occur due to low coolant levels, a faulty radiator, a damaged water pump, or poor airflow in the cooling system. Regular maintenance helps prevent such issues.


 in Cars.webp)


