If you have ever come across the term "drivetrain" when purchasing a car, it refers to the crucial components and shafts that work simultaneously to make your wheels turn.
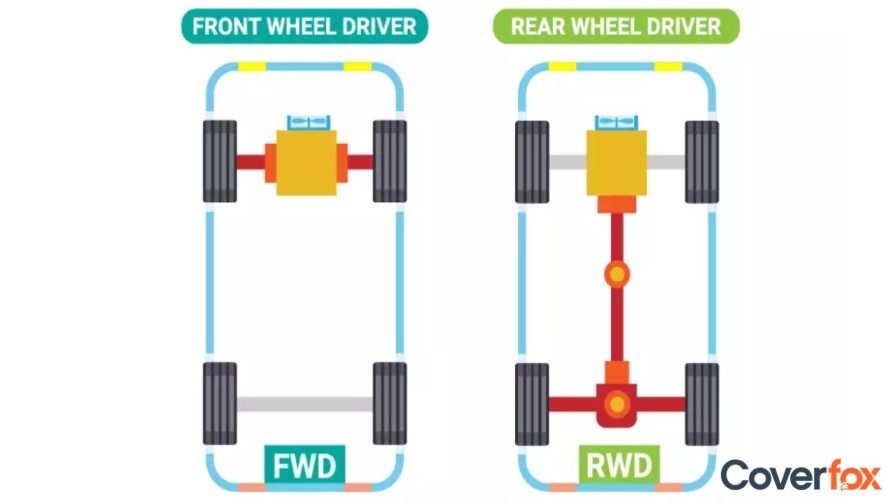
Among the four drive variants available, such as front wheel drive, rear wheel drive, all wheel drive, and 4 wheel drive, vehicles most commonly use the Front-Wheel Drive (FWD) and Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD) systems. However, there is a difference between them that is important to understand to help you choose the right car for your needs.
To understand these concepts in detail, the guide below takes you through what Front Wheel Drive and Rear Wheel Drive mean, their pros and cons, the main difference between Front Wheel Drive and Rear Wheel Drive, and which one may be better suited for you.
What Is Front Wheel Drive (FWD)?
Front-Wheel Drive, or FWD, is the drivetrain setup that transfers engine power to the front two wheels of the vehicle, allowing them to move and steer. For vehicles, FWD has been used since the 1930s and is considered cheaper to manufacture and more space-saving than RWD. Cars with this drivetrain are an ideal option to use during the rainy season.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Front Wheel Drive
Check out the various pros and cons of owning a vehicle with a Front Wheel Drive (FWD):
| Advantages of FWD | Disadvantages of FWD |
|---|---|
| The engine and transmission sit above the front wheels, giving better grip on hills and slippery roads. | Extra weight in the front can cause understeer while turning. |
| Compact design creates more cabin and legroom in the back. | Fast acceleration may cause “torque steer”, pulling the car left or right. |
| Fewer parts make the car lighter and more fuel-efficient. | Lower towing capacity compared to RWD or AWD cars. |
| The steering wheel gives clearer feedback if the wheels slip. | Slower acceleration than RWD, making it less sporty. |
| Simple system, cheaper to buy and maintain. | Weight at the front can make handling less balanced. |
| Works well in dry, rainy, and light snow conditions with ABS and traction control. | CV joints and boots wear out faster than in RWD cars. |
What Is Rear Wheel Drive (RWD)?
In contrast to FWD, a Rear-Wheel Drive, or RWD, is a drivetrain configuration where the engine power is transferred to the two rear wheels of the vehicle with the help of an elongated driveshaft. Cars with this drivetrain turn out to be more reliable while travelling across rough terrain, as they help deliver superior handling, acceleration, and braking.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Rear Wheel Drive
Before opting for a vehicle with Rear Wheel Drive (RWD), check out the multiple pros and cons it offers:
| Advantage of Rear Wheel Drive | Disadvantage of Rear Wheel Drive |
|---|---|
| Handles better in dry conditions because of balanced weight and power transfer. | Harder to control for new drivers, though stability systems help. |
| Easier and cheaper to maintain since parts are not packed tightly. | Less cabin space due to the driveshaft and transmission tunnel. |
| No “torque steer”, which is common in front-wheel drive cars. | Smaller trunk space because of extra equipment at the rear. |
| Good for towing heavy loads, as the rear wheels push while the front wheels steer. | Heavier than FWD because of the driveshaft. |
| Easier to drift compared to FWD or AWD (not recommended for daily use). | Slightly higher cost to buy. |
| Popular in sports cars for better performance. | Poor grip in rain and snow, unless supported by traction control. |
Major Differences Between Front Wheel Drive and Rear Wheel Drive
To help ease your understanding, have a look at the table below highlighting the key differences between Front Wheel Drive vs Rear Wheel Drive:
| Aspect | Front Wheel Drive (FWD) | Rear Wheel Drive (RWD) |
|---|---|---|
| Weight Balance | Weight is mostly at the front, not evenly spread. | Weight is more evenly balanced across the car. |
| Gearbox & Clutch Layout | The gearbox, clutch, and differential are combined into one unit. | The gearbox and clutch are built separately. |
| Luggage Space | More space for luggage at the rear. | Less luggage space due to the driveshaft and differential. |
| Performance on Slopes | Can understeer on slippery or uphill surfaces. | Works better on slopes with more control. |
| Drivetrain Components | The differential is placed at the front; the design helps keep the floor lower. | Differential and long driveshafts take up more space, raising the floor. |
| Traction & Grip | Good overall grip, especially when cornering. | Lower grip compared to FWD; can slip more easily. |
| Weight on Wheels | Front wheels carry more weight, improving traction. | Less weight on the rear wheels and may skid on slippery surfaces. |
| Complexity & Maintenance | Simpler design, cheaper and easier to maintain. | More complex, may require higher maintenance. |
| Driving Conditions | Best for city driving, dry and rainy conditions, and light snow. | Strong in performance driving but needs caution on slippery surfaces. |
| Vehicle Type | Common in budget-friendly and daily-use cars. | Found in sports cars, luxury cars, and performance-focused vehicles. |
| Examples | Toyota Corolla, Honda Civic | BMW 3 Series, Ford Mustang. |
Conclusion
In the end, the debate between Front Wheel Drive vs Rear Wheel Drive rests on one’s own preferences and needs. Both have their own unique advantages and disadvantages. Since FWD vehicles are lighter in weight and more fuel efficient, they are mostly suitable for driving on city streets or during rainy conditions. On the other hand, RWD vehicles have a balanced weight across the vehicle and can drive on various terrains.
Since FWD vehicles have a simpler design, they may be easier to maintain; however, RWD vehicles require higher maintenance. This can end up having an impact on the car insurance policy premiums. To select the car insurance policy suited for your vehicle drivetrain type, whether FWD or RWD, head to Coverfox for a plan that fits both your budget and your needs.
Now you can see how different drivetrain types affect a vehicle’s performance and price. They can also influence the cost of a comprehensive car insurance policy and the Insured Declared Value (IDV) in car insurance.
Also Read:
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Front Wheel Drive & Rear Wheel Drive?
In FWD, the engine’s power goes to the front wheels, which handle both driving and steering. In RWD, the power is sent to the rear wheels while the front wheels only steer.
Which is safer, Front Wheel Drive or Rear Wheel Drive?
Front Wheel Drive (FWD) vehicles are considered safer, especially in wet and slippery conditions, as they provide better grip with the engine and transmission sitting above the front wheels.
Does Rear-Wheel Drive use more fuel than front wheel drive?
Yes, Rear Wheel Drive (RWD) vehicles are said to use more fuel as compared to Front Wheel Drive (FWD) vehicles.
Which vehicles use Rear-Wheel Drive?
Rear Wheel Drive is mostly used in vehicles like sports cars, luxury cars, and performance-focused vehicles.


 in Cars.webp)


