MCWG vs LMV distinctions significantly influence driving licence endorsements and vehicle insurance requirements under the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988. LMV MCWG categories define permissible vehicle classes, ensuring road safety through appropriate authorisation.
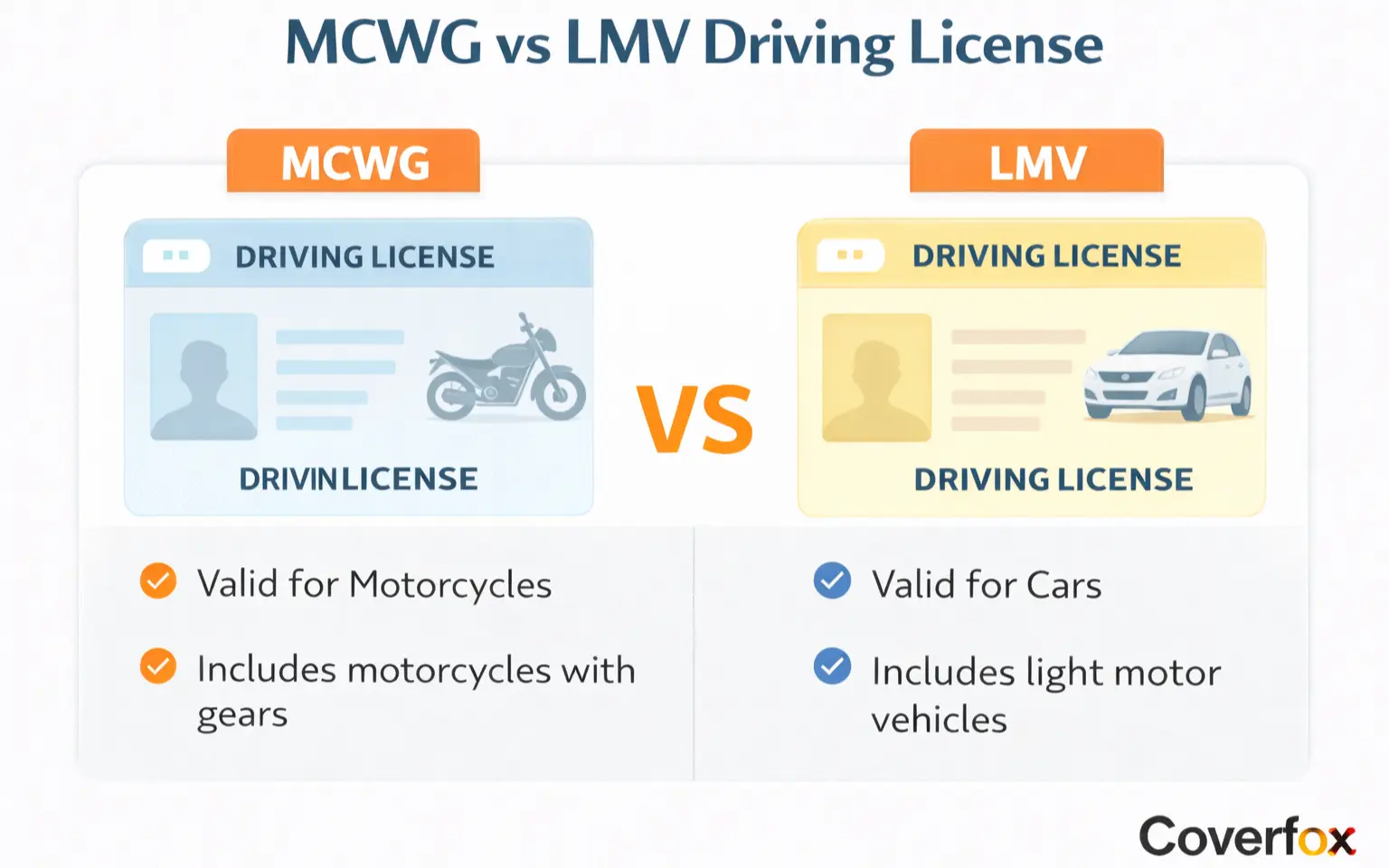
MCWG and LMV Meaning
MCWG LMV full form expands to Motorcycle with Gear for MCWG and Light Motor Vehicle for LMV. MCWG in driving licence authorises geared two-wheelers up to 50cc engine capacity, while LMV in driving licence permits non-commercial four-wheelers under 7.5 tonnes gross vehicle weight. These endorsements appear on the reverse of the driving licence under vehicle class codes.
Key Difference Between MCWG and LMV Driving Licence
Driving licence categories impose strict vehicle restrictions:
| Category | Full Form | Vehicles Allowed | Engine Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCWG | Motorcycle with Gear | Geared motorcycles, scooters | Up to 50cc |
| LMV | Light Motor Vehicle | Cars, jeeps, taxis (private) | Up to 7.5 tonnes GVW |
LMV and MCWG: Vehicle Classifications
LMV and MCWG align with the Central Motor Vehicles Rules, 1989:
MCWG
LMV
Geared two-wheelers excluding mopeds (engine >50cc requires separate endorsement).
Private cars, vans carrying up to 13 persons, light trucks under 7.5 tonnes.
Commercial vehicles demand transport licences beyond these classes.
Insurance for MCWG vs LMV
Insurance obligations differ by category:
MCWG Insurance
Mandatory third-party bike insurance covers rider and bike liability.
Comprehensive insurance adds own-damage protection for theft and accidents.
Premiums range from ₹1,500 to ₹ 4,000 annually for 125cc bikes.
LMV Insurance
Third-party car insurance is mandatory for cars, and higher rates are due to vehicle value.
Comprehensive car insurance is essential for cars above ₹5 lakh, including zero-depreciation.
| Aspect | MCWG | LMV |
|---|---|---|
| Mandatory Cover | Third-party | Third-party |
| Premium Range | Low (₹1,500+) | Higher (₹7,000+) |
| Add-ons | Engine protect | Zero dep., NCB |
An invalid licence voids claims under comprehensive insurance.
Driving Licence Application Process for LMV & MCWG
Applicants secure endorsements through:
Submit Form 2 with the learner's application to RTO.
Pass the theory test (20/50 marks).
Complete 30-hour training for LMV, 20 hours for MCWG.
Clear road test by Motor Vehicle Inspector.
Renewals every 20 years post-50 age require medical fitness.
Penalties for Category Violations
Driving vehicles without a proper MCWG or LMV endorsement attracts strict penalties:
₹5,000 fine under Section 181 MV Act for first offence
Licence suspension of 3-6 months for repeat violations within 3 years
Insurance claim denial – both third-party insurance and comprehensive insurance rejected
Vehicle impoundment for commercial vehicle violations under Section 192
₹10,000 fine for repeat commercial vehicle offences
Personal liability for all accident damages and third-party claims
Potential criminal charges for persistent violations leading to accidents
MCWG vs LMV: Practical Implications
LMV and MCWG choices impact daily use:
MCWG suits urban commuting on geared bikes.
LMV enables family cars for highway travel.
Upgrade via endorsement test without full reapplication.
Also Read:
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. Driving licence rules, vehicle classifications, penalties, and insurance requirements are subject to the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988, Central Motor Vehicles Rules, 1989, and state-specific RTO regulations, which may change over time. Insurance premiums, coverage, and claim eligibility vary by insurer, vehicle, and policy terms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on MCWG vs LMV
Are LMV and MCWG the same?
No, LMV covers light four-wheelers under 7.5 tonnes gross vehicle weight, including private cars and jeeps. MCWG limits authorisation to geared motorcycles up to 50cc engine capacity only. Distinct endorsements prevent cross-operation legally.
Can MCWG drive a four-wheeler?
No, the MCWG in the driving licence restricts holders exclusively to two-wheelers with manual transmission. Four-wheeler operation demands a separate LMV endorsement under the Motor Vehicles Act provisions. Violations incur ₹5,000 fines and insurance claim invalidation.
Does LMV include scooters?
LMV excludes all two-wheelers, including scooters, from its scope entirely. Geared scooters require MCWG endorsement, while gearless models fall under the MCWOG category. Separate classifications ensure vehicle-specific training and testing.
What is the MCWG LMV full form?
MCWG denotes Motorcycle with Gear; LMV signifies Light Motor Vehicle as defined in the Central Motor Vehicles Rules, 1989. These codes appear on the reverse side of driving licences, indicating authorised vehicle classes.
Is third-party insurance sufficient for LMV?
Third-party insurance meets the statutory minimum requirements for LMV vehicles under the Motor Vehicles Act. However, comprehensive insurance provides essential own-damage protection against accidents, theft, and natural calamities prevalent with cars.
How to upgrade from MCWG to LMV?
Submit Form 2A at RTO for additional endorsement, complete the required training hours, and pass the LMV driving skills evaluation by a Motor Vehicle Inspector. Existing MCWG holders require no theory retest for upgrade. Processing completes within 30 days.


 in Cars.webp)

