A piston is a core engine component that converts the energy produced by fuel combustion into mechanical motion that drives a vehicle. Moving up and down inside the engine cylinder, it enables power generation through the four-stroke cycle.
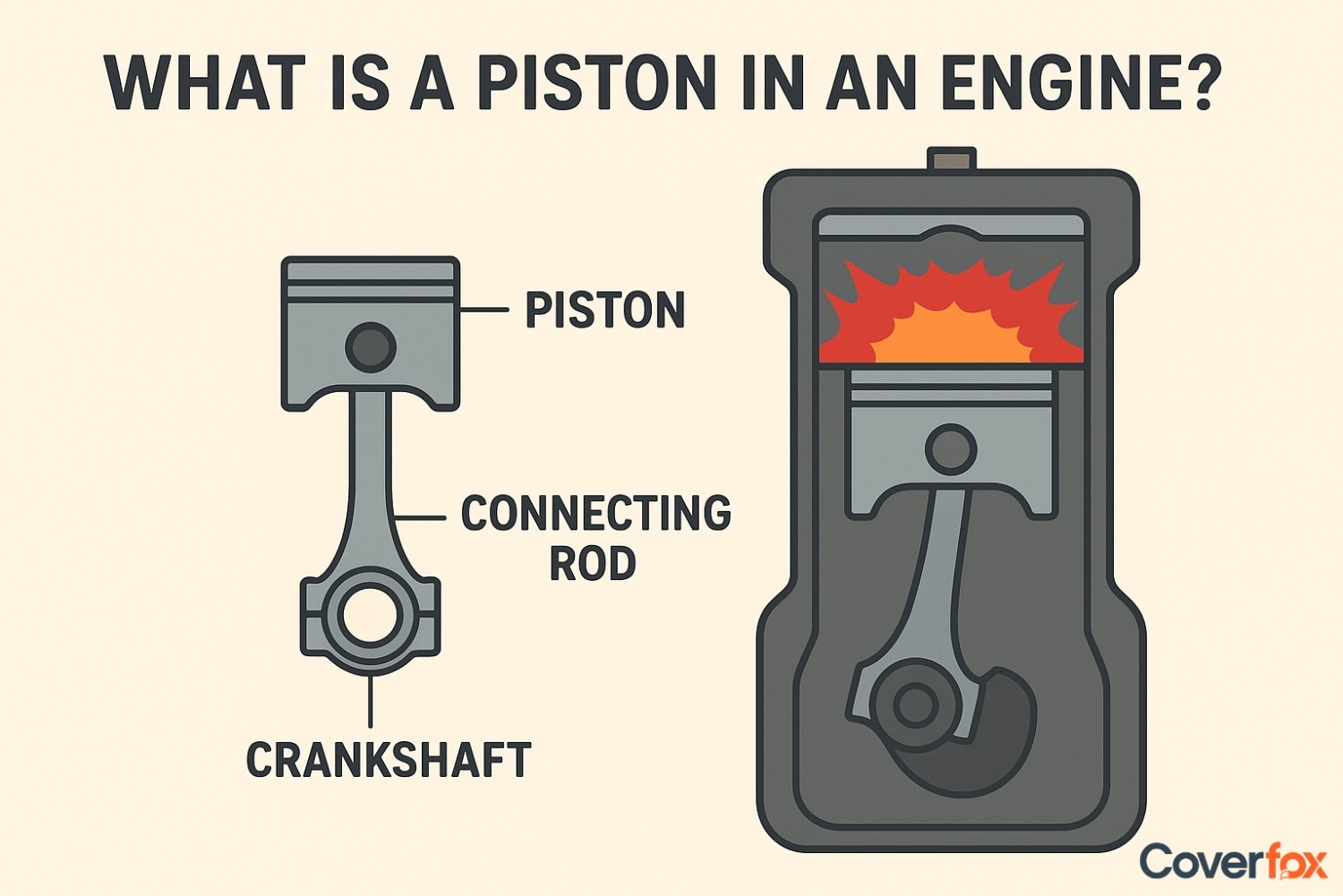
Ever seen a syringe work? When you push the plunger down, it creates pressure, and when you pull it up, it draws fluid in. A piston works in a similar way inside a car engine, moving up and down to create pressure and power. A piston is a cylindrical part inside the engine that moves up and down to convert fuel combustion into mechanical energy. In this article, we’ll explain how a piston works in a car engine, its types, functions, and why it is essential for smooth vehicle performance.
What is a Piston?
A piston is a cylindrical component fitted inside the engine cylinder that moves up and down during the combustion process. Its main function is to transfer the force generated by the burning of fuel to the crankshaft, which then converts this energy into motion to drive the vehicle. Basically, it is an essential part involved in creating rotational energy that helps move the car.
Material and Design of a Piston
Pistons are commonly made from aluminium alloys because they are lightweight, strong, and conduct heat efficiently, making them ideal for everyday engines. High-performance engines use forged aluminium or steel pistons for greater strength under high temperatures and pressure.
The design of a piston factors in piston shape, crown design, skirt length, and ring grooves, which affect how efficiently fuel burns, how well heat is dissipated, and how smoothly the piston moves inside the cylinder. Performance engines often use lightweight, precisely shaped pistons to reduce friction and increase power output, while everyday vehicles use more durable designs focused on longevity and fuel economy.
Types of Piston Engine
Piston engines are classified based on their design, fuel type, and working mechanism, each suited for different vehicle and performance needs.
Single-Cylinder Engine
Multi-Cylinder Engine
Inline Engine
V-Type Engine
Opposed (Flat) Engine
Petrol and Diesel Engines
Uses one piston; commonly found in small bikes and scooters.
Uses two or more pistons for smoother performance; common in cars and larger vehicles.
Cylinders arranged in a straight line, offering good balance and efficiency.
Cylinders arranged in a V shape, used in high-performance and luxury vehicles.
Pistons move horizontally in opposite directions, improving balance and stability.
Classified based on fuel type and combustion method.
How Does a Piston Work in an Engine?
This is how a piston works to convert fuel energy into the power that moves a vehicle.
1. Intake Stroke
The piston moves downward, drawing in the air–fuel mixture into the cylinder.
2. Compression Stroke
The piston moves upward, compressing the mixture to prepare it for ignition.
3. Power Stroke
The spark plug ignites the mixture, causing an explosion that pushes the piston down with force.
4. Exhaust Stroke
The piston moves up again to push out burnt gases, making the cylinder ready for the next cycle.
This continuous up-and-down motion of the piston powers the engine and keeps the vehicle running smoothly.
Components of Pistons
A piston is made up of several important parts that work together to ensure smooth engine operation and efficient power generation.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Piston Crown | Top surface that receives combustion pressure. |
| Piston Skirt | Guides piston movement inside the cylinder. |
| Piston Rings | Seal combustion gases and control oil flow. |
| Ring Grooves | Hold the piston rings in place. |
| Wrist Pin | Connects piston to the connecting rod. |
| Connecting Rod End | Transfers piston motion to the crankshaft. |
Key Properties of a Good Piston
A good piston must survive extreme heat and pressure while moving thousands of times per minute, without losing strength, shape, or balance.
High strength
Lightweight design
Good heat resistance
Durability
Balanced construction
Low-friction movement
The piston must withstand extreme pressure and heat during combustion without cracking or deforming.
A lighter piston reduces engine load, improves fuel efficiency, and allows smoother engine operation.
Since pistons operate at very high temperatures, they must handle heat efficiently without expanding excessively.
A good piston resists wear and tear, ensuring long engine life and consistent performance.
Proper balance helps reduce vibration, noise, and stress on other engine parts.
Smooth surface finish and design help the piston move freely inside the cylinder, improving efficiency and reducing damage.
Common Piston Issues
Pistons operate under extreme heat and pressure, which can lead to several common problems over time if maintenance is poor or the engine is overworked.
1. Piston wear
Continuous friction can cause the piston or rings to wear out, leading to loss of compression.
2. Piston overheating
Excess heat may cause the piston to expand excessively, leading to scuffing or seizure.
3. Cracked or damaged piston
High combustion pressure or poor fuel quality can cause cracks or holes in the piston.
4. Piston ring failure
Worn or broken rings can result in oil burning, smoke, and reduced engine performance.
5. Piston slap
Occurs when there is excess clearance between the piston and cylinder, causing noise during engine operation.
6. Carbon buildup
Deposits on the piston crown can affect combustion efficiency and engine performance.
Wrapping Up
Like every other engine component, the piston plays an important role in generating rotational energy that helps the car move. Although it often goes unnoticed, a faulty piston can lead to serious issues such as engine failure, difficulty starting the car, or even breakdowns that affect your safety. To stay protected from unexpected repair costs and disruptions, it’s wise to have a reliable car insurance policy in place.
Articles to Read:
Engine Decarbonisation: What It Is and Why Your Car Needs It
Internal and External Combustion Engines: What You Need to Know
NOS in Cars: Legal Guidelines, Risks, and Benefits
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a piston in an engine?
A piston is a cylindrical component inside the engine that moves up and down to convert fuel energy into mechanical power.
What materials are pistons made from?
Pistons are usually made from aluminium alloys due to their lightweight and heat-resistant properties. High-performance engines may use forged aluminium or steel pistons.
Where is the piston located?
The piston is located inside the engine cylinder and is connected to the crankshaft through a connecting rod.
How does a piston work?
The piston moves up and down inside the cylinder during intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes to generate engine power.
What are piston rings used for?
Piston rings seal the combustion chamber, control oil flow, and help transfer heat from the piston to the cylinder walls.
How many strokes does a piston complete in a cycle?
In a four-stroke engine, the piston completes four strokes: intake, compression, power, and exhaust.
Can an engine run without a piston?
No, an engine cannot run without a piston as it is essential for converting fuel energy into motion.
What happens if a piston fails?
A damaged piston can cause engine misfiring, loss of power, excessive smoke, or complete engine failure.
Do pistons affect engine efficiency?
Yes, piston design and condition directly affect engine efficiency, fuel consumption, and performance.
What is the function of pistons?
The main function of a piston is to convert the pressure created by fuel combustion into mechanical energy that powers the vehicle