Gone are the days when you had to spin the wheel just to make a left or a right turn. Power steering wheels have revolutionised the entire steering system in the car. It has made turning or reversing a car so much easier – no need to work out arm muscles to drive the car!
So what exactly is power steering, and how does it work? Read on to find out!
What is a Power Steering System?
A power steering system is a vehicle mechanism that assists the driver in turning the steering wheel with minimal effort. Its core purpose is to reduce the physical strain required for steering, especially at low speeds or during parking. Using hydraulic, electric, or electro-hydraulic assistance, it offers smoother, more precise control and greatly enhances comfort and driving ease compared to traditional manual steering systems.
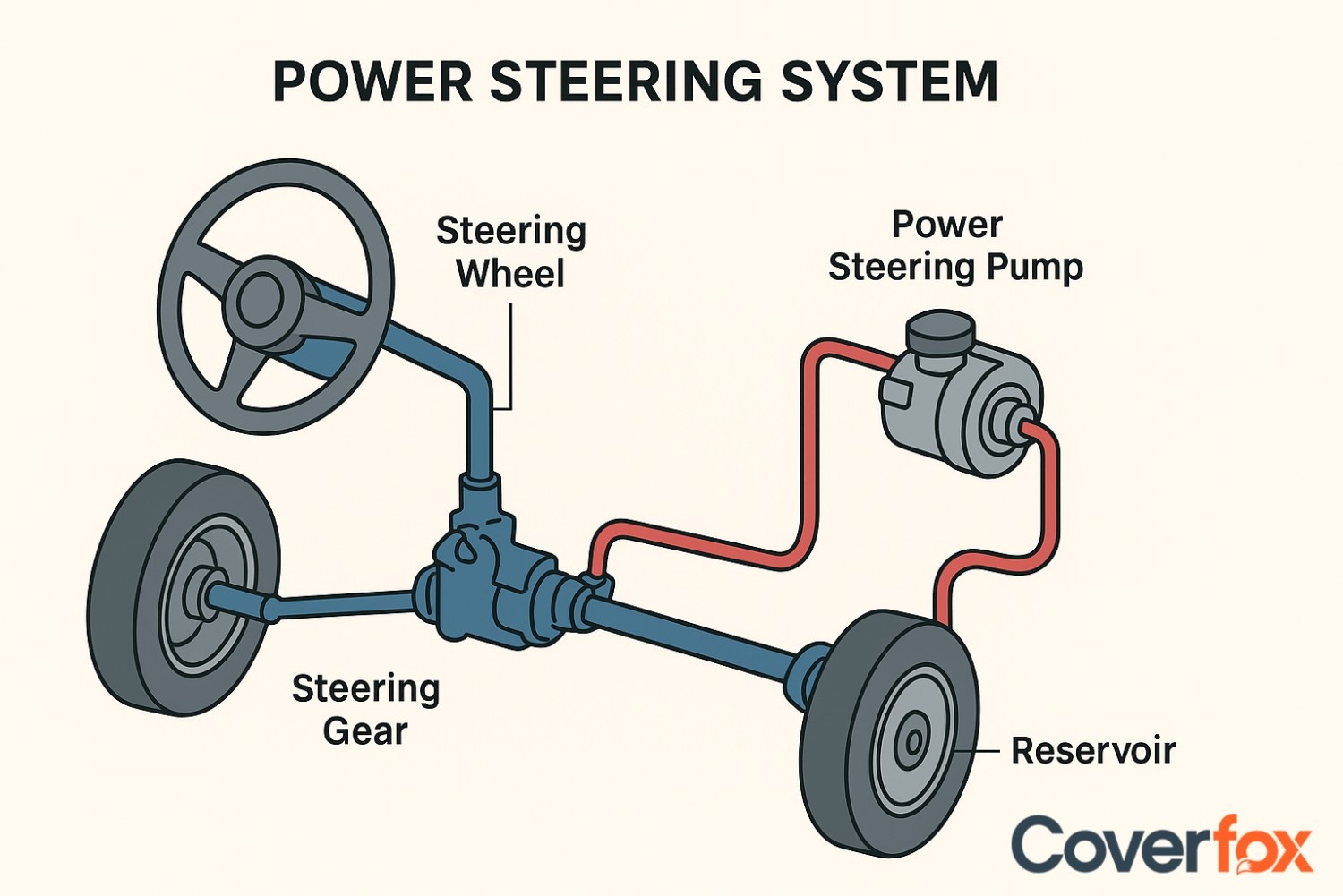
Basic Components of a Power Steering System
Here is the list of components that help form a power steering system in a car:
Steering Wheel and Column
Steering Gearbox or Rack and Pinion
Power Steering Pump
Hydraulic Fluid Reservoir
Hoses and Lines
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Electric Motor (in EPS)
The driver’s input device that initiates steering movement.
Transfers motion from the steering wheel to the wheels.
Generates hydraulic pressure (in hydraulic systems) to assist steering.
Stores and supplies fluid to maintain consistent pressure.
Carry hydraulic fluid between the pump, reservoir, and steering gear.
In electric systems, it controls motor assistance based on driving conditions.
Provides the necessary torque assistance without hydraulic fluid.
How Power Steering Works?
Power steering works by using hydraulic or electric assistance to reduce the effort needed to turn the steering wheel:
1. Driver Input
When the driver turns the steering wheel, sensors or valves detect the movement and direction.
2. Assistance Activation
In hydraulic systems, the power steering pump sends pressurised fluid to assist wheel movement; in electric systems, a motor provides torque assistance.
3. Force Amplification
The system multiplies the driver’s input force, making it easier to turn the wheels.
4. Wheel Movement
The amplified force is transmitted through the steering gearbox or rack and pinion to steer the vehicle’s wheels.
5. Feedback Control
The system continuously adjusts assistance based on speed and steering angle for smooth, stable handling.
Types of Power Steering Systems
There are several types of power steering systems, each designed to make steering smoother and more efficient using different technologies:
Integral Power Steering
Linkage Power Steering
Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS)
Electric Power Steering (EPS)
Electro-Hydraulic Power Steering (EHPS)
Combines the steering gearbox and hydraulic assist mechanism into one unit, providing direct and responsive steering control commonly found in heavy vehicles.
Uses mechanical linkages connected to a hydraulic cylinder that assist the steering arm, often used in commercial or off-road vehicles for added strength and durability.
Utilises a hydraulic pump driven by the engine to generate pressure, which assists steering through fluid force—effective but less fuel-efficient.
Employs an electric motor controlled by sensors and an ECU to provide variable steering assistance based on speed and driving conditions—lightweight and energy-efficient.
Combines both systems, using an electric motor to drive the hydraulic pump, offering the smooth feel of hydraulics with the efficiency and adaptability of electric control.
Advantages of Power Steering Systems
The biggest benefit of power steering is that it minimises the effort it takes to steer the vehicle. Other than that, these are the advantages of a power steering system in a car:
- Reduces driver effort, especially at low speeds or while parking.
- Enhances driving comfort and control.
- Improves vehicle handling and manoeuvrability.
- Provides quicker and more precise steering response.
- Reduces driver fatigue during long journeys.
- Increases overall driving safety and stability
Power Steering vs. Manual Steering
Power steering has replaced manual steering in modern-day cars. Here's how they stand out from a traditional steering system:
| Feature | Power Steering | Manual Steering |
|---|---|---|
| Steering Effort | Requires minimal effort to turn the wheel | Requires more physical effort, especially at low speeds |
| Comfort | Provides smoother and more comfortable driving | It can be tiring during long drives or tight manoeuvres |
| Control | Offers better control and precise handling | Less responsive, especially in larger vehicles |
| Technology | Uses hydraulic, electric, or electro-hydraulic assistance | Purely mechanical linkage without assistance |
| Cost | Higher initial cost and slightly higher maintenance | Lower cost and simpler maintenance |
Electric Steering vs Hydraulic Power Steering
As power steering comes in different types, it is important to understand the difference between the 2 most common steering systems – electric and hydraulic:
| Feature | Electric Power Steering (EPS) | Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Assistance Mechanism | Uses an electric motor to provide steering support | Uses a hydraulic pump driven by the engine to assist steering |
| Energy Efficiency | More fuel-efficient as it draws power only when needed | Less efficient due to continuous engine-driven pump operation |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance with fewer moving parts | Requires regular checks of hydraulic fluid, hoses, and the pump |
| Steering Feel | Can be tuned electronically for variable assistance | Provides natural hydraulic feedback, but is less adjustable |
| Cost | Slightly higher initial cost for technology integration | Generally lower upfront cost, but may incur fluid/pump maintenance costs |
| Application | Common in modern cars, SUVs, and electric vehicles | Traditional vehicles and some heavy-duty applications |
Common Problems with Power Steering
Power steering systems, while enhancing driving comfort, can encounter issues over time due to wear, leaks, or component failure.
- Low power steering fluid is causing stiff steering.
- Leaking hoses or seals reduce hydraulic pressure.
- Worn pump leading to whining noises.
- Faulty electric motor causing loss of assist.
- Steering rack issues resulting in jerky movement.
- Loose or worn belts affect pump efficiency.
Summary
Power steering is an indispensable feature in modern vehicles, enhancing driving comfort, control, and safety. Advancements from hydraulic to electric systems have improved efficiency, precision, and ease of handling. Just as power steering ensures safe driving, car insurance, including third-party coverage, is essential for legal compliance and responsible vehicle ownership.
Also Read:
Differences Between Front Wheel Drive (FWD) & Rear Wheel Drive (RWD)
Regenerative Braking: What It Is and How It Works
High Security Number Plates (HSRPs): A Complete Guide
Frequently Asked Questions
What is power steering and its types?
Power steering is a system that assists the driver in steering the vehicle with less effort. Its types include hydraulic, electric, electro-hydraulic, integral, and linkage systems.
What are the 5 functions of a steering system?
The steering system controls vehicle direction, provides stability, transmits driver input to wheels, absorbs road shocks, and ensures safe manoeuvring.
How often do we need to check the power steering fluid level?
It is recommended to check the fluid level at least once a month or during routine vehicle servicing.
Where is power steering used?
Power steering is used in cars, SUVs, trucks, buses, and some heavy machinery to reduce steering effort and improve handling.
How do I know if my car has hydraulic or electric power steering?
Check the owner’s manual or look for a hydraulic pump and fluid reservoir (HPS) or an electric motor connected to the steering column or rack (EPS).
Can I drive without power steering?
Yes, but steering will require significantly more effort, especially at low speeds, making it harder to manoeuvre safely.
Which type of power steering is more common in modern cars?
Electric Power Steering (EPS) is the most common in modern cars due to its efficiency, low maintenance, and adaptability.

 in Car.webp)



