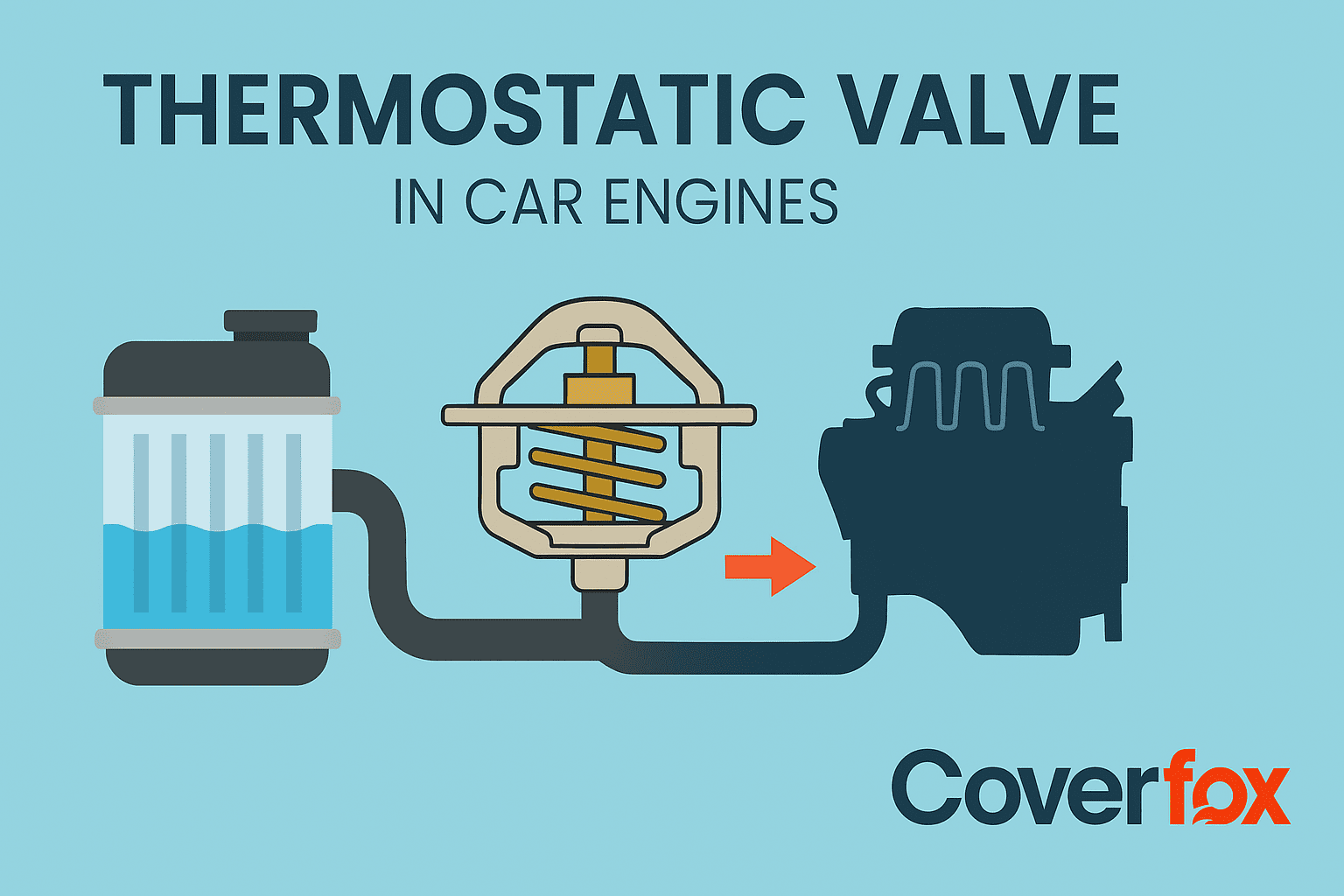
Just as a thermostat is used in homes to maintain a cool and pleasant temperature around the house, car engines also require one such tool. Located between the engine cooling system and the radiator, a thermostatic valve is a temperature regulator for the car, preserving and maintaining the inner core parts of the engine.
Let us learn more about different types of thermostatic valves, and their functioning in a car engine.
What is a Thermostatic Valve?
A thermostatic valve in a car is a key component of the engine’s cooling system that regulates coolant flow based on engine temperature. It remains closed when the engine is cold, allowing it to warm up quickly, and opens as the engine reaches optimal operating temperature to let coolant circulate to the radiator. This ensures the engine runs efficiently, prevents overheating, and maintains stable performance. By controlling temperature, it also helps reduce wear and improve fuel efficiency.
How the Thermostatic Valve Operates
The thermostatic valve operates by sensing the engine’s temperature and adjusting the coolant flow accordingly. Here’s how it functions within a car’s cooling system:
Temperature Detection
Cold Start
Opening Phase
Coolant Circulation
Automatic Adjustment
The valve contains a wax pellet that expands when heated, detecting changes in engine temperature.
When the engine is cold, the valve stays closed, preventing coolant from circulating to help the engine warm up faster. This ensures less fuel is consumed and is backed by research (Study on Enhancing vehicle’s engine warm up using integrated mechanical approach)
As the engine reaches its optimal operating temperature (usually around 85–90°C), the expanding wax pushes a piston that opens the valve.
The open valve allows coolant to flow through the radiator, releasing excess heat and maintaining a steady temperature.
The valve continuously adjusts its position to balance temperature fluctuations, ensuring consistent engine performance.
Functions of Thermostatic Valves?
Thermostatic valves perform several crucial roles in maintaining the engine’s efficiency and longevity.
- Regulate engine temperature for optimal performance.
- Prevent overheating by controlling coolant flow.
- Allow faster engine warm-up during cold starts.
- Improve fuel efficiency by maintaining ideal operating conditions.
- Reduce engine wear caused by temperature fluctuations.
- Support emission control by ensuring consistent combustion temperature.
Different Types of Thermostatic Valves
There are several types of thermostatic valves used in cars, each designed for specific cooling system needs.
1. Wax Pellet Thermostat
The most common type, using a wax element that expands with heat to open the valve. Bypass Thermostat: Directs coolant flow through a bypass when the engine is cold and redirects it to the radiator once warmed up.
2. Sleeve Valve Thermostat
Uses a sliding sleeve mechanism to control the flow between the radiator and bypass circuit.
3. Electronic Thermostat
Controlled by the engine control unit (ECU) for more precise temperature management and better fuel efficiency.
4. Dual Thermostat
Found in modern engines, it uses two thermostats to separately regulate temperature for different engine sections or cooling circuits.
Common Issues with Thermostatic Valves
A faulty thermostat valve can significantly affect a car’s performance by disrupting the engine’s temperature regulation. If it gets stuck open, the engine may run too cold, reducing efficiency and increasing fuel consumption. If it remains closed, the engine can overheat, leading to severe damage like warped cylinders or gasket failure. Timely inspection and replacement are crucial to avoid costly repairs. Here are some common issues that you can find about thermostatic valves in cars: A valve stuck open causes poor fuel efficiency and slow warm-up.
- A valve stuck closed leads to overheating and potential engine damage.
- Corrosion or debris buildup restricts smooth valve operation.
- The faulty wax element fails to expand properly, affecting temperature control.
- Leakage around the valve housing reduces cooling efficiency.
- Inaccurate sensor signals in electronic thermostats cause irregular temperature management.
How to Test and Diagnose a Faulty Thermostatic Valve
As a faulty thermostatic valve can damage your car’s engine or disrupt the fuel efficiency of the car, it is important to test and diagnose at regular intervals for any damaged or faulty valves. You can do so by:
Temperature Monitoring
Coolant Flow Check
Touch Test
Boiling Water Test
OBD Diagnostic Scan
Visual Inspection
Check if the engine takes too long to warm up or overheats quickly — both indicate thermostat issues.
With the engine running, observe the radiator; if coolant doesn’t flow when hot, the valve may be stuck closed.
Feel the radiator hose — it should remain cool during warm-up and gradually heat up once the thermostat opens.
Remove the thermostat and place it in hot water to see if it opens around the specified temperature (usually 85–90°C).
In modern cars, scan the ECU for temperature-related fault codes indicating thermostat or sensor problems.
Look for corrosion, deposits, or damage on the valve housing that could affect its function.
Wrapping Up
The thermostatic valve is a critical component that ensures the engine maintains optimal temperature, preventing overheating or running too cold. Regular maintenance keeps the engine efficient, reduces emissions, and improves fuel economy. Combined with comprehensive four-wheeler insurance, it provides financial protection against repairs and accidents, ensuring both the engine and your investment remain well safeguarded.
Also Read:
Regenerative Braking: What It Is and How It Works
Differences Between Front Wheel Drive (FWD) & Rear Wheel Drive (RWD)
Understanding the Different Types of Crankshafts & Their Functions
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a thermostatic valve in a car engine?
A thermostatic valve is a component in the cooling system that regulates coolant flow based on engine temperature, ensuring the engine operates at an optimal level.
What happens when a thermostat valve fails?
A faulty valve can cause the engine to overheat or run too cold, leading to poor performance, increased fuel consumption, or potential engine damage.
Can a car run without a thermostat?
While technically possible, running without a thermostat leads to inefficient engine temperature control, longer warm-up times, higher fuel use, and increased engine wear.
What are the signs of a bad thermostatic valve?
Common signs include engine overheating, unusually long warm-up times, fluctuating temperature gauge readings, and poor heater performance.
Can I drive with a faulty thermostatic valve?
It is not recommended, as it can cause engine overheating or inefficient performance, potentially resulting in severe engine damage.
Where is the thermostatic valve located?
It is usually located between the engine and the radiator, often near the water outlet of the engine block.
Why is the thermostatic valve important?
It maintains optimal engine temperature, improving fuel efficiency, reducing emissions, and preventing engine damage.
Does every car have a thermostatic valve?
Most modern cars have a thermostatic valve, though the type and design may vary depending on the engine and cooling system.
Is the thermostatic valve hot or cold?
It starts cold when the engine is warming up and gradually opens as it heats to allow coolant flow, regulating temperature automatically.

 in Car.webp)



