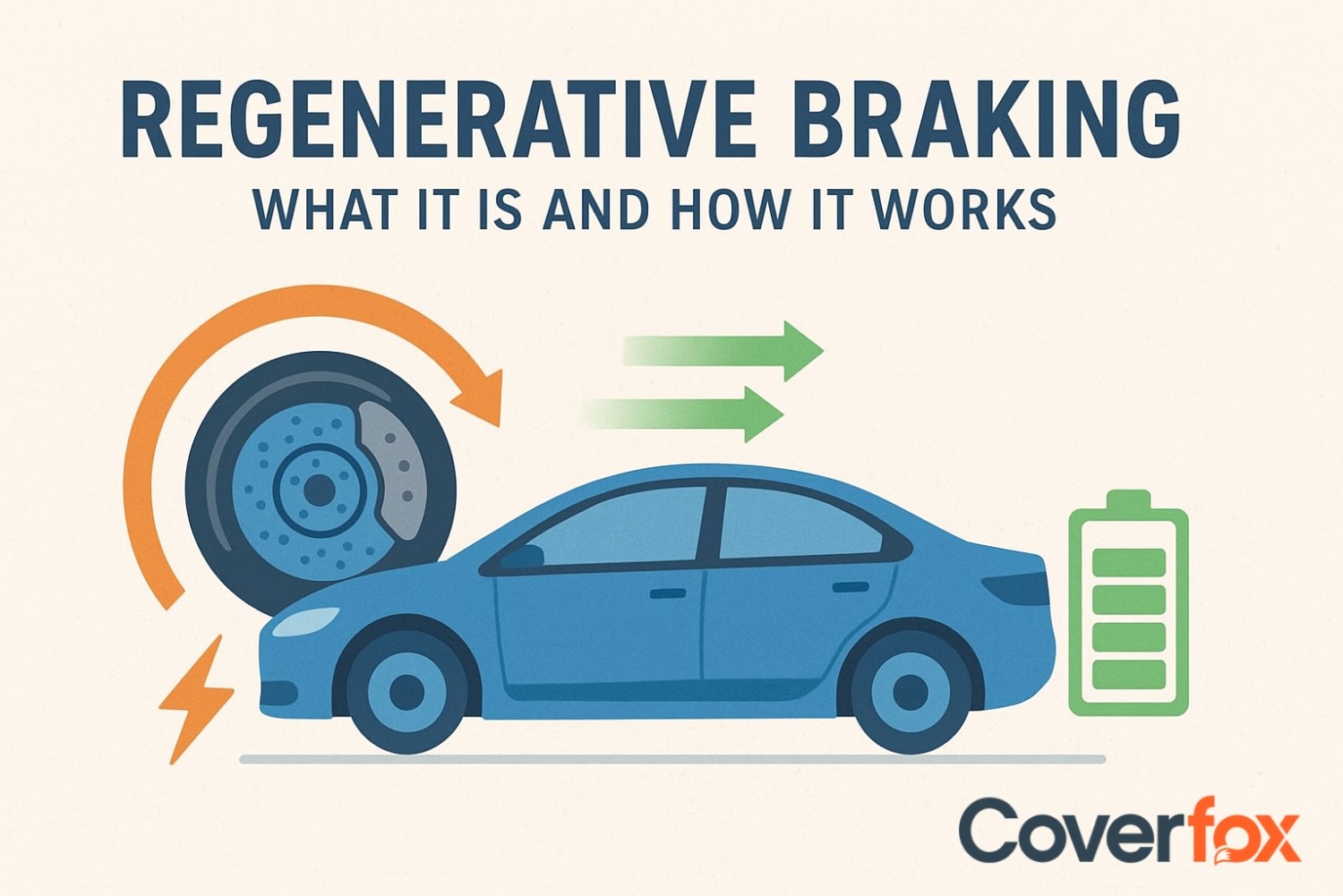
“Regenerative Braking” is a buzzword that has been stuck along with the evolution of Electric Vehicles, hybrids and plugin EVs. It is a system designed to improve power consumption efficiency, fuel efficiency in hybrids, and take a load off the engine.
So what exactly is engine braking, and how does it work? This article will fulfill all your queries about this system.
What is Regenerative Braking?
Regenerative Braking is a technology used in electric vehicles (EVs), hybrid vehicles, and some modern trains to recover energy that would otherwise be lost as heat during braking. Instead of relying solely on friction brakes, the system allows the electric motor to act as a generator when the vehicle slows down. This process converts the vehicle’s kinetic energy into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery for later use.
The concept of regenerative braking was first proposed by French electrical engineer M. A. Darracq in 1889, but the earliest known practical application came from American inventor Charles Kettering in 1908, who developed early systems for electric vehicles. Later, it was widely adopted in trains and trams in the early 20th century (notably by the London Underground in the 1930s). The first ever car to use engine braking was the Toyota Prius, which is a hybrid EV.
Need for Regenerative Braking
As vehicles become more energy-conscious, regenerative braking plays a crucial role in improving efficiency and sustainability. It helps not only in extending the vehicle’s range but also in reducing wear on traditional braking systems. Here’s why:
Energy Recovery
Extended Driving Range
Reduced Fuel Consumption
Lower Emissions
Less Wear and Tear
Efficiency in Stop-Go Traffic
Regenerative braking stores kinetic energy that would normally be wasted as heat and converts it into electricity. This stored energy can later power the vehicle, improving overall efficiency.
By reusing energy, EVs and hybrids can travel longer distances on the same charge or fuel. This is especially beneficial for long commutes and urban driving.
In hybrid vehicles, regenerative braking reduces dependence on the internal combustion engine. This leads to lower fuel usage and cost savings over time.
Since less fuel is burned in hybrids, regenerative braking helps cut down on harmful emissions. This makes it a vital feature for greener and more sustainable transport.
With part of the braking load handled by the electric motor, friction brakes are used less often. This prolongs brake life and reduces maintenance costs.
Frequent braking in city conditions allows maximum energy regeneration. This makes regenerative braking highly effective in urban environments.
How Does Regenerative Braking Work?
Regenerative braking converts the vehicle’s motion into usable electrical energy during deceleration. Instead of losing all the kinetic energy as heat, part of it is stored back into the battery, making the system more efficient. Here is a step-by-step process on how a regenerative braking system works:
1. The Driver Initiates Braking
When the accelerator is released or the brake pedal is pressed, the vehicle’s control system decides how much of the braking force can be provided through regeneration.
2. Motor Switches to Generator Mode
The traction motor, normally responsible for propulsion, reverses its role and begins acting as a generator, resisting wheel rotation to slow the vehicle.
3. Kinetic Energy Conversion
The vehicle’s kinetic energy, instead of being wasted as heat, is converted into electrical energy by the generator action of the motor.
4. Power Regulation
Power electronics and converters regulate the generated electricity, adjusting voltage and current so it is safe and suitable for charging the battery.
5. Energy Storage in a Battery
The regulated electricity is directed into the battery pack, where it is stored for future use, effectively recycling the energy.
6. Blending with Friction Brakes
If additional braking force is needed (such as during sudden stops or when the battery is full), the system automatically uses traditional friction brakes to ensure safety and control.
Key Components of Regenerative Braking Systems
The components involved in the process of electrical engine braking are:
Electric Motor / Generator
Power Electronics (Inverter/Converter)
Battery Pack
Battery Management System (BMS)
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Friction Brakes
Brake Pedal & Sensors
Functions as both the drive motor and a generator. During braking, it converts the vehicle’s kinetic energy into electrical energy.
Regulates the motor’s output, converting variable AC into DC electricity that is suitable for battery charging.
Stores the recovered electrical energy, which can later be used to power the vehicle during acceleration or normal driving.
Ensures safe charging by monitoring temperature, voltage, and current while preventing overcharging or damage.
Acts as the decision-maker, balancing regenerative and friction braking to provide safe and efficient stopping.
Traditional disc or drum brakes that provide additional stopping power when regenerative braking alone is not enough.
Capture driver input and send signals to the ECU, helping determine how much braking should come from regeneration versus friction.
Different Types of Regenerative Braking
There are multiple types of regenerative braking, like:
1. Series Regenerative Braking
In this type, the electric motor is the primary source of braking. When the driver slows down, the motor converts kinetic energy into electricity, which is stored in the battery. Friction brakes are used only when additional stopping power is needed or at very low speeds. Example: Some early electric vehicles and simple EV systems use series regenerative braking.
2. Parallel Regenerative Braking
Here, regenerative braking works with traditional friction brakes at the same time. Both systems slow down the vehicle, ensuring smoother deceleration and better control. Energy recovery happens continuously, while safety is maintained. Example: Some hybrid vehicles use parallel braking for city driving conditions.
3. Blended (Series–Parallel) Regenerative Braking
This is the most common system in modern EVs and hybrids. It intelligently balances or blends regenerative braking with friction brakes based on speed, battery state-of-charge, and driver input. This approach maximises energy recovery while maintaining predictable braking feel. Example: Toyota Prius and Tesla models use blended regenerative braking.
4. Plug-in Regenerative Braking
Used mainly in electric trains, trams, and some advanced EV setups, this system allows braking energy to be fed back into the external power grid when the onboard battery is full or cannot accept more energy. It enhances overall energy efficiency and reduces wastage. Example: Modern metro trains with regenerative systems that feed energy back to the grid.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Regenerative Braking
While regenerative braking is a reformation in the braking systems and EVs, this breakthrough also has some setbacks:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Captures kinetic energy and stores it in the battery. | Cannot provide full braking power in emergencies. |
| Extends the driving range of EVs and hybrids. | Less effective at very low speeds. |
| Reduces fuel consumption and emissions. | Effectiveness is limited when the battery is full. |
| Minimises wear on friction brakes, lowering maintenance costs. | Increases vehicle cost due to complex electronics. |
| Maximises efficiency in stop-and-go traffic. | Different braking feels may require driver adjustment. |
Future Developments in Regenerative Braking Technology
Regenerative braking is enhancing energy efficiency in Indian EVs by capturing and storing up to 70% of braking energy, especially in urban traffic, which extends vehicle range and reduces energy consumption. Emerging technologies like AI and digital twins are being integrated to optimise energy recovery in real time. The system is now standard across two-wheelers, three-wheelers, and passenger EVs, improving efficiency and lowering operating costs. Initiatives like solar-powered EV charging hubs in India further support regenerative braking by providing clean energy for charging.
Emerging Technologies:
Solid-State Batteries
Wireless Charging Systems
Predictive Maintenance Models
The development of solid-state batteries promises higher energy densities and faster charging times. These advancements complement regenerative braking by providing more efficient energy storage solutions.
Wireless charging technologies are being explored to eliminate the need for physical connectors, offering convenience and potentially integrating with regenerative braking systems for seamless energy transfer.
AI-driven predictive maintenance models are being developed to monitor the health of regenerative braking systems. These models can predict component wear and optimise performance, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Summing Up
As EV stands for efficiency and sustainability, regenerative braking helps achieve the objectives of an EV. It helps reduce braking strain, stores kinetic energy that would have been otherwise wasted, and helps the efficiency of the engine. Regenerative braking systems act as a helping hand to EVs, adding to the already attractive benefits an EV has. While regenerative braking has its own benefits, it is important to secure your EV with car insurance to ensure your financial safety if the brakes fail on you!
Also Read:
Types of Brakes and Braking Systems in Automobiles
Differences Between Front Wheel Drive (FWD) & Rear Wheel Drive (RWD)
Multi Point Fuel Injection (MPFI) in Vehicles
Frequently Asked Questions
Is regenerative braking available in all cars?
No, it is primarily available in electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicles. Conventional petrol or diesel cars do not have regenerative braking.
Is regenerative braking AC or DC?
The motor typically generates AC electricity, which is then converted to DC by the vehicle’s power electronics to charge the battery.
Does regenerative braking affect driving range?
Yes, by recovering energy that would otherwise be lost as heat, regenerative braking can extend the driving range of EVs and hybrids.
How effective is regenerative braking during highway driving?
It is less effective at high speeds because most energy recovery occurs during stop-and-go conditions, such as city traffic.
Does regenerative braking replace normal brakes?
No, it works alongside traditional friction brakes. Friction brakes are still needed for emergency stops and full braking power.
Is regenerative braking only for electric vehicles?
Primarily, yes. It is used in EVs, hybrids, and electric trains, though conventional ICE vehicles use engine braking instead.
Does regenerative braking work at all speeds?
Regenerative braking is most effective at moderate to low speeds. At very low speeds, its contribution decreases, and friction brakes take over.